bistrifluron
Modify Date: 2025-08-20 12:05:32
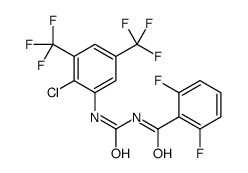
bistrifluron structure
|
Common Name | bistrifluron | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 201593-84-2 | Molecular Weight | 446.68 | |
| Density | 1.606g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H7ClF8N2O2 | Melting Point | 172 - 175°C (lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS09 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of bistrifluronBistrifluron has insecticidal effects on the larval stage, and also has an effect on adult longevity, reproduction, and hatchability. Bistrifluron is used for the control of a variety of Lepidopterous pests[1]. |
| Name | bistrifluron |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Bistrifluron has insecticidal effects on the larval stage, and also has an effect on adult longevity, reproduction, and hatchability. Bistrifluron is used for the control of a variety of Lepidopterous pests[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.606g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Melting Point | 172 - 175°C (lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C16H7ClF8N2O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 446.68 |
| Exact Mass | 446.00700 |
| PSA | 65.18000 |
| LogP | 6.20610 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.515 |
| 1-[2-Chloro-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea |
| Bistrifluron |
| 1-[2-chloro-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]-3-(2,6-difluorobenzoyl)urea |
| N-[[2-chloro-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide |
| N-{[2-chloro-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]carbamoyl}-2,6-difluorobenzamide |
| N-[[[2-chloro-3,5-bis(trifluoromethyl)phenyl]amino]carbonyl]-2,6-difluorobenzamide |