UCL 1684
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 14:21:24
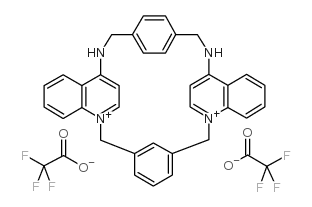
UCL 1684 structure
|
Common Name | UCL 1684 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 199934-16-2 | Molecular Weight | 720.66000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C38H30F6N4O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of UCL 1684UCL 1684 (dibromide) is a first nanomolar, non-peptidic small conductance calcium-activated potassium (SK) channel blocker. UCL 1684 (dibromide) is effective in preventing the development of atrial fibrillation due to potent atrial-selective inhibition of INa. UCL 1684 (dibromide) causes atrial-selective prolongation of ERP secondary to induction of postrepolarization refractoriness[1][2][3]. |
| Name | UCL 1684,6,12,19,20,25,26-Hexahydro-5,27:13,18:21,24-trietheno-11,7-metheno-7H-dibenzo[b,n][1,5,12,16]tetraazacyclotricosine-5,13-diiumdibromide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | UCL 1684 (dibromide) is a first nanomolar, non-peptidic small conductance calcium-activated potassium (SK) channel blocker. UCL 1684 (dibromide) is effective in preventing the development of atrial fibrillation due to potent atrial-selective inhibition of INa. UCL 1684 (dibromide) causes atrial-selective prolongation of ERP secondary to induction of postrepolarization refractoriness[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Potassium Channel[1] |
| In Vitro | UCL 1684 (dibromide) (0.5 μM; HEK cells) produces direct atrial-selective inhibition of sodium channel current (INa) and shifts SS inactivation of the cardiac sodium channels. UCL 1684 (dibromide) (0.5 μM) induces PRR, decreases V max, increases DTE, and extends the shortest S1-S1 interval[1]. |
| In Vivo | UCL 1684 (dibromide) (3 mg/kg; i.v.) increases wenckebach cycle length to 115.0±5.1 % of baseline value[3]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C38H30F6N4O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 720.66000 |
| Exact Mass | 720.21700 |
| PSA | 112.08000 |
| LogP | 5.07540 |
| ucl 1684 |