Kumbicin C
Modify Date: 2025-08-27 10:17:58
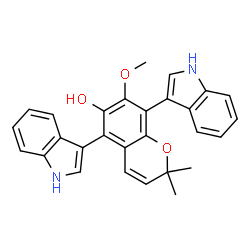
Kumbicin C structure
|
Common Name | Kumbicin C | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1878151-58-6 | Molecular Weight | 436.502 | |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 710.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C28H24N2O3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 383.7±32.9 °C | |
Use of Kumbicin CKumbicin C is a bis-indolyl benzenoid compound from an Australian soil fungus, Aspergillus kumbius. Kumbicin C inhibits the growth of mouse myeloma cells and the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis[1]. |
| Name | Kumbicin C |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Kumbicin C is a bis-indolyl benzenoid compound from an Australian soil fungus, Aspergillus kumbius. Kumbicin C inhibits the growth of mouse myeloma cells and the Gram-positive bacterium Bacillus subtilis[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.3±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 710.8±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C28H24N2O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 436.502 |
| Flash Point | 383.7±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 436.178680 |
| LogP | 4.97 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.707 |
| InChIKey | XQUDQEFLDBAHTH-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | COc1c(O)c(-c2c[nH]c3ccccc23)c2c(c1-c1c[nH]c3ccccc13)OC(C)(C)C=C2 |
| 2H-1-Benzopyran-6-ol, 5,8-di-1H-indol-3-yl-7-methoxy-2,2-dimethyl- |
| 5,8-Di(1H-indol-3-yl)-7-methoxy-2,2-dimethyl-2H-chromen-6-ol |
| Kumbicin C |