N-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline
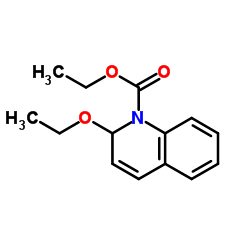
N-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline structure
|
Common Name | N-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 16357-59-8 | Molecular Weight | 247.290 | |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 355.9±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H17NO3 | Melting Point | 62-67 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 169.0±27.9 °C | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
| Name | N-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 355.9±42.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 62-67 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C14H17NO3 |
| Molecular Weight | 247.290 |
| Flash Point | 169.0±27.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 247.120850 |
| PSA | 38.77000 |
| LogP | 2.98 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.565 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Water Solubility | insoluble |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H315 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful; |
| Risk Phrases | R20/21/22;R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S22-S24/25-S36/37/39-S26 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | VB2010000 |
| HS Code | 29334990 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 4 | |
| HS Code | 2933499090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933499090. other compounds containing in the structure a quinoline or isoquinoline ring-system (whether or not hydrogenated), not further fused. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Monoamine receptor agonists, acting preferentially at presynaptic autoreceptors and heteroreceptors, downregulate the cell fate adaptor FADD in rat brain cortex.
Neuropharmacology 89 , 204-14, (2014) FADD is a crucial adaptor of death receptors that can engage apoptosis or survival actions (e.g. neuroplasticity) through its phosphorylated form (p-FADD). Although FADD was shown to participate in re... |
|
|
Dengue type four viruses with E-Glu345Lys adaptive mutation from MRC-5 cells induce low viremia but elicit potent neutralizing antibodies in rhesus monkeys.
PLoS ONE 9(6) , e100130, (2014) Knowledge of virulence and immunogenicity is important for development of live-attenuated dengue vaccines. We previously reported that an infectious clone-derived dengue type 4 virus (DENV-4) passaged... |
|
|
Evidence for segregation of sphingomyelin and cholesterol during formation of COPI-coated vesicles.
J. Cell Biol. 151 , 507-18, (2000) In higher eukaryotes, phospholipid and cholesterol synthesis occurs mainly in the endoplasmic reticulum, whereas sphingomyelin and higher glycosphingolipids are synthesized in the Golgi apparatus. Lip... |
| 1-Ethoxycarbonyl-2-ethoxy-1,2-dihydroquinoline |
| 2-Ethoxy-1-ethoxycarbonyl-1,2-dihydroquinoline |
| 1(2H)-Quinolinecarboxylic acid, 2-ethoxy-, ethyl ester |
| Ethyl 1,2-dihydro-2-ethoxyquinoline-1-carboxylate |
| 2-Ethoxy-1(2H)-quinolinecarboxylic Acid Ethyl Ester |
| EEDQ |
| EINECS 240-418-2 |
| Ethyl-2-ethoxychinolin-1(2H)-carboxylat |
| ethyl 2-ethoxy-2H-quinoline-1-carboxylate |
| 2-Ethoxy-1-ethoxycarbonyl-1,2-dihydroquinoline (EEDQ) |
| ethyl 2-ethoxyquinoline-1(2H)-carboxylate |
| MFCD00006703 |
| Ethyl 2-ethoxy-1(2H)-quinolinecarboxylate |
 CAS#:91-22-5
CAS#:91-22-5 CAS#:64-17-5
CAS#:64-17-5 CAS#:3783-38-8
CAS#:3783-38-8 CAS#:3673-34-5
CAS#:3673-34-5
