HTHQ
Modify Date: 2025-08-23 19:06:13
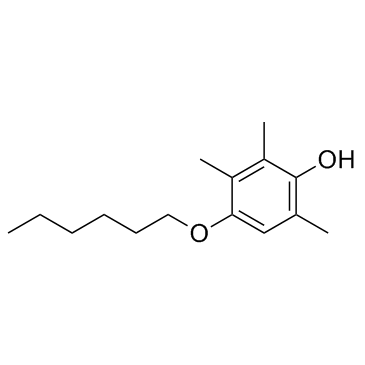
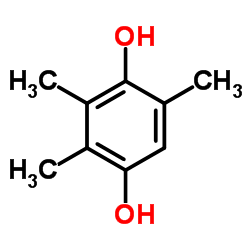
HTHQ structure
|
Common Name | HTHQ | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 148081-72-5 | Molecular Weight | 236.35 | |
| Density | 0.971g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 357.8ºC at 760mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C15H24O2 | Melting Point | 72.5-73ºC | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | 154.4ºC | |
Use of HTHQHTHQ, which is a hydroquinone monoalkyl ether, is a potent anti-oxidative agent, even at low dose levels.HTHQ is found to be a potent anti-lipid-peroxidative compound and its antioxidation activity to be extremely elevated in biological systems, such as that of liver microsomes via the generation of stable free radicals. In vitro: HTHQ exhibits a similar anti-oxidative activity to that of D,L-alpha-tocopherol against lipid peroxidation in linolate micelles initiated by addition of Fe2+. HTHQ exhibits approximately 4.8-fold higher anti-lipid-peroxidation activity than that of D,L-alpha-tocopherol against the peroxidation in phosphatidylcholine liposomes initiated by addition of Fe2+. [1] up to 0.125% HTHQ significantly reduced the effects of 0.02% Glu-P-1 or 0.03% MeIQx on the number and area of foci. [2]In vivo: Treatment with HTHQ potently inhibits PhIP-induced mammary carcinogenesis in female rats without prior initiation treatment. . HTHQ administration shows reduced mRNA level of PDGF (Plateletderived growth factor) , α-SMA (α-smooth muscle actin) and TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) than DMN-induced hepetic fibrosis animals in the liver tissue. In this study, we showed that HTHQ improves against DMN-induced liver fibrosis in male SD rats.[3] |
| Name | 4-hexoxy-2,3,6-trimethylphenol |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | HTHQ, which is a hydroquinone monoalkyl ether, is a potent anti-oxidative agent, even at low dose levels.HTHQ is found to be a potent anti-lipid-peroxidative compound and its antioxidation activity to be extremely elevated in biological systems, such as that of liver microsomes via the generation of stable free radicals. In vitro: HTHQ exhibits a similar anti-oxidative activity to that of D,L-alpha-tocopherol against lipid peroxidation in linolate micelles initiated by addition of Fe2+. HTHQ exhibits approximately 4.8-fold higher anti-lipid-peroxidation activity than that of D,L-alpha-tocopherol against the peroxidation in phosphatidylcholine liposomes initiated by addition of Fe2+. [1] up to 0.125% HTHQ significantly reduced the effects of 0.02% Glu-P-1 or 0.03% MeIQx on the number and area of foci. [2]In vivo: Treatment with HTHQ potently inhibits PhIP-induced mammary carcinogenesis in female rats without prior initiation treatment. . HTHQ administration shows reduced mRNA level of PDGF (Plateletderived growth factor) , α-SMA (α-smooth muscle actin) and TGF-β (transforming growth factor-β) than DMN-induced hepetic fibrosis animals in the liver tissue. In this study, we showed that HTHQ improves against DMN-induced liver fibrosis in male SD rats.[3] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 0.971g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 357.8ºC at 760mmHg |
| Melting Point | 72.5-73ºC |
| Molecular Formula | C15H24O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 236.35 |
| Flash Point | 154.4ºC |
| PSA | 29.46000 |
| LogP | 3.60910 |
| Vapour Pressure | 1.29E-05mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.507 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
|
~64% 
HTHQ CAS#:148081-72-5 |
| Literature: Wang; Furukawa; Nihro; Kakegawa; Matsumoto; Satoh Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1994 , vol. 42, # 3 p. 570 - 575 Title/Abstract Full Text View citing articles Show Details Nihro; Furukawa; Sogawa; Wang; Miyataka; Matsumoto; Miki; Satoh Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin, 1994 , vol. 42, # 3 p. 576 - 579 |
|
~% 
HTHQ CAS#:148081-72-5 |
| Literature: Hoppe-Seyler's Zeitschrift fuer Physiologische Chemie, , vol. 254, p. 39,41 |
| Precursor 3 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |
| 3-Hydroxy-6-hexyloxy-1.2.4-trimethyl-benzol |
| HTHQ |
| DSSTox_CID_697 |
| 1-O-n-hexyl-2,3,5-trimethylhydroquinone |
| 4-Hexyloxy-2,3,6-trimethyl-phenol |
| 1-O-Hexyl-2,3,5-trimethylhydroquinone |
| HTHQ-2,3,5 |