PD123319 di(trifluoroacetate)
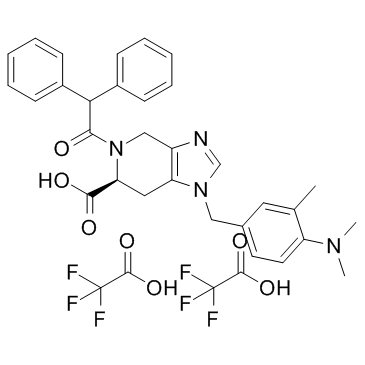
PD123319 di(trifluoroacetate) structure
|
Common Name | PD123319 di(trifluoroacetate) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 136676-91-0 | Molecular Weight | 736.657 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C35H34F6N4O7 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
Signal Word | Warning | |
Use of PD123319 di(trifluoroacetate)PD 123319 (ditrifluoroacetate) is a potent, selective AT2 angiotensin II receptor antagonist with IC50 of 34 nM. |
| Name | PD 123319 bistrifluoroacetate |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | PD 123319 (ditrifluoroacetate) is a potent, selective AT2 angiotensin II receptor antagonist with IC50 of 34 nM. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 34 nM (AT2 Receptor)[1] |
| In Vitro | PD 123319 is shown to discriminate between two subclasses of AII receptors in many different tissues. 125I-AII specifically label two classes of binding sites for AII in a membrane preparation of bovine adrenal glomerulosa cells. The first class (DuP-753 sensitive) represents approximately 85% of the total binding sites for AII and possesses a high affinity (IC50 of 92.9 nM) for DuP-753. PD-123319 does not have any effect on 125I-AII binding to this site. The second class of binding sites is more sensitive to PD-123319, with an IC50 of 6.9 nM, and has a much lower affinity for DuP-753 (IC50 around 10 microM)[2]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C35H34F6N4O7 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 736.657 |
| Exact Mass | 736.233154 |
| PSA | 115.97000 |
| LogP | 5.04700 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |
| Symbol |

GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Warning |
| Hazard Statements | H315-H319-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|
Contractility of placental vascular smooth muscle cells in response to stimuli produced by the placenta: roles of ACE vs. non-ACE and AT1 vs. AT2 in placental vessel cells.
Placenta 29(6) , 503-9, (2008) Our previously published work has shown that non-ACE angiotensin II (Ang II) generating system is dominate in the placenta and may play a critical role in regulation of placental vascular contractile ... |
|
|
Modulation of angiotensin II binding affinity by allosteric interaction of polyvinyl sulfate with an intracellular domain of the DuP-753-sensitive angiotensin II receptor of bovine adrenal glomerulosa.
Mol. Pharmacol. 41 , 809-815, (1992) Angiotensin II (AII) is an important regulator of aldosterone secretion by adrenal glomerulosa cells. All interacts with a specific receptor coupled to a guanine nucleotide-binding protein that contro... |
|
|
Differential blockade of central effects of angiotensin II by AT2-receptor antagonists.
Am. J. Physiol. 265 , H226, (1993) In conscious, chronically instrumented, male Long-Evans rats, we showed previously that central administration (intracerebroventricular) of the AT1-receptor antagonist EXP-3174 (1 microgram) caused a ... |
| 1H-Imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid, 1-[[4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl]methyl]-5-(2,2-diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-, (6S)- |
| (S)-1-<<4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl>methyl>-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo<4,5-c>pyridine-6-carboxylic acid |
| (6S)-1-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-methylbenzyl]-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid trifluoroacetate (1:2) |
| S-(+)-1-[(4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl)methyl]-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid di(trifluoroacetate) |
| 1H-Imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid, 1-[[4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl]methyl]-5-(2,2-diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-, (6S)-, compd. with 2,2,2-trifluoroacetic acid (1:2) |
| (3S)-9-[(4-DIMETHYLAMINO-3-METHYL-PHENYL)METHYL]-4-(2,2-DIPHENYLACETYL)-4,7,9-TRIAZABICYCLO[4.3.0]NONA-7,10-DIENE-3-CARBOXYLIC ACID |
| 1-((4-(Dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl)methyl)-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[4.5-c]pyridine-6-carboxyli |
| PD 123,319 DITRIFLUOROACETATE |
| pd 123,319 di(trifluoroacetate) salt |
| 1H-Imidazo(4,5-c)pyridine-6-carboxylic acid, 1-((4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl)methyl)-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-, (S)- |
| S-(+)-1-((4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl)methyl)-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazol(4,5-c)pyridine-6-carboxylic acid |
| (S)-1-((4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl)methyl)-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo(4,5-c)pyridine-6-carboxylic acid,difluoroacetate salt |
| (6S)-1-[4-(Dimethylamino)-3-methylbenzyl]-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid |
| (S)-1-{[4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl]methyl}-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo[4,5-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid |
| PD 123,319 |
| (S)-1-{[4-(dimethylamino)-3-methylphenyl]methyl}-5-(diphenylacetyl)-4,5,6,7-tetrahydro-1H-imidazo-[4,5-c]pyridine-6-carboxylic acid,ditrifluoroacetate,dihydrate |
| PD 123319 (ditrifluoroacetate) |