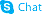Osteocalcin (1-49) (human) acetate salt
Modify Date: 2024-01-10 17:43:34

Osteocalcin (1-49) (human) acetate salt structure
|
Common Name | Osteocalcin (1-49) (human) acetate salt | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 136461-80-8 | Molecular Weight | 5929.43 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C269H381N67O82S2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Osteocalcin (1-49) (human) acetate saltOsteocalcin (1-49) (human) is a vitamin K-dependent bone specific protein. Osteocalcin (1-49) (human) is chemotactic for several of the cell types frequently found at bone remodeling surfaces[1][2]. |
| Name | H-TYR-LEU-TYR-GLN-TRP-LEU-GLY-ALA-PRO-VAL-PRO-TYR-PRO-ASP-PRO-LEU-GLA-PRO-ARG-ARG-GLA-VAL-CYS-GLA-LEU-ASN-PRO-ASP-CYS-ASP-GLU-LEU-ALA-ASP-HIS-ILE-GLY-PHE-GLN-GLU-ALA-TYR-ARG-ARG-PHE-TYR-GLY-PRO-VAL-OH |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Osteocalcin (1-49) (human) is a vitamin K-dependent bone specific protein. Osteocalcin (1-49) (human) is chemotactic for several of the cell types frequently found at bone remodeling surfaces[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Up to 20% of all non-collagenous protein in human bone consists of Osteocalcin. Only minor amounts of Osteocalcin are secreted into the blood circulation where it can be measured by immunochemical methods[1]. Osteocalcin in serum is supposedly derived from newly synthesized bone, and the amount of this protein in serum may be a very specific marker for bone formation rate[1]. Osteocalcin (1 nM-1 μM) is chemotactic for breast cancer cells and osteoblast-like osteogenic sarcoma cells as well as monocytes, and causes their unidirectional migration[2]. Osteocalcin peptide contains 49 amino acids, with subsequent breakdown to fragments 1–19, 20–49, 20–43, 1–43, and 44–49 in the liver, kidney, and serum[3]. |
| Molecular Formula | C269H381N67O82S2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 5929.43 |
| Appearance of Characters | solid |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
|---|---|
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
Deletion of connexin43 in osteoblasts/osteocytes leads to impaired muscle formation in mice.
J. Bone Miner Res. 30(4) , 596-605, (2015) It is well-established that muscle forces are necessary for bone development as well as proper bone modeling and remodeling. Recent work has also suggested that bone acts as an endocrine organ that ca... |
| TYR-LEU-TYR-GLN-TRP-LEU-GLY-ALA-PRO-VAL-PRO-TYR-PRO-ASP-PRO-LEU-GLA-PRO-ARG-ARG-GLA-VAL-CYS-GLA-LEU-ASN-PRO-ASP-CYS-ASP-GLU-LEU-ALA-ASP-HIS-ILE-GLY-PHE-GLN-GLU-ALA-TYR-ARG-ARG-PHE-TYR-GLY-PRO-VAL (DISULFIDE BRIDGE: CYS23-CYS29) |