Patulin-13C7
Modify Date: 2025-08-25 11:56:30
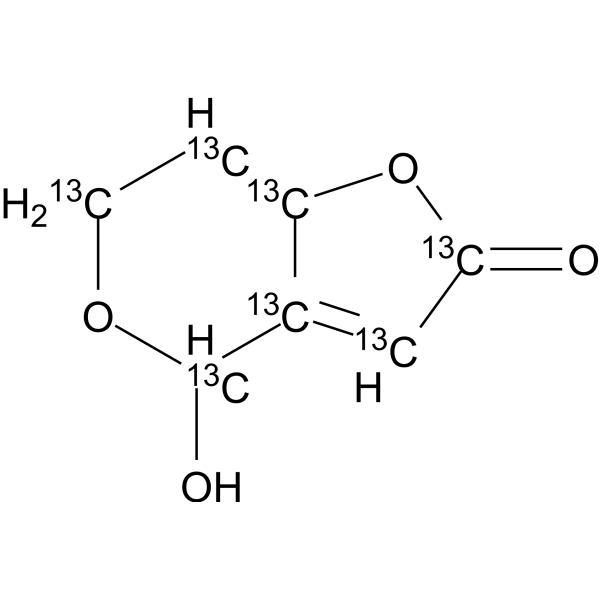
Patulin-13C7 structure
|
Common Name | Patulin-13C7 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1353867-99-8 | Molecular Weight | 161.07 | |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | 13C7H6O4 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Patulin-13C7Patulin-13C7 (Terinin-13C7) is the 13C labeled Patulin (HY-N6779)[1]. Patulin (Terinin) is a mycotoxin produced by fungi including the Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Byssochlamys species, is suspected to be clastogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic and cytotoxic. Patulin induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis through lysosomal-mitochondrial axis, and causes DNA damage[2][3][4][5]. |
| Name | MFCD17018964 |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Patulin-13C7 (Terinin-13C7) is the 13C labeled Patulin (HY-N6779)[1]. Patulin (Terinin) is a mycotoxin produced by fungi including the Aspergillus, Penicillium, and Byssochlamys species, is suspected to be clastogenic, mutagenic, teratogenic and cytotoxic. Patulin induces autophagy-dependent apoptosis through lysosomal-mitochondrial axis, and causes DNA damage[2][3][4][5]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 氢、碳和其他元素的稳定重同位素已被纳入药物分子中,主要作为药物开发过程中定量的示踪剂。氘化引起了人们的关注,因为它可能影响药物的药代动力学和代谢谱[1]。 |
| References |
| Density | 1.5±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | 13C7H6O4 |
| Molecular Weight | 161.07 |
| Exact Mass | 161.050095 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.603 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Hazard Codes | F+ |
|---|
| MFCD17018964 |
| Patulin-13C7 solution |
| 4H-Furo[3,2-c]pyran-2(6H)-one-2,3,3a,4,6,7,7a-13C7, 4-hydroxy- |
| 4-Hydroxy(13C7)-4H-furo[3,2-c]pyran-2(6H)-one |
| 4-Hydroxy-4H-furo[3,2-c]pyran-2(6H)-one-13C7 |
| Patulin-13C7 |
| EINECS 200-835-2 |