1,6-Hexanediamine

1,6-Hexanediamine structure
|
Common Name | 1,6-Hexanediamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 124-09-4 | Molecular Weight | 116.20500 | |
| Density | 0.89 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 204-205 °C | |
| Molecular Formula | C6H16N2 | Melting Point | 42-45 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 201 °F | |
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | hexane-1,6-diamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.89 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 204-205 °C |
| Melting Point | 42-45 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C6H16N2 |
| Molecular Weight | 116.20500 |
| Flash Point | 201 °F |
| Exact Mass | 116.13100 |
| PSA | 52.04000 |
| LogP | 1.86480 |
| Vapour density | 4 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0821mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | n20/D 1.439(lit.) |
| InChIKey | NAQMVNRVTILPCV-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | NCCCCCCN |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, strong acids, organic materials. |
| Water Solubility | 490 g/L (20 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |


GHS05, GHS07 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302 + H312-H314-H335 |
| Precautionary Statements | P301 + P312 + P330-P303 + P361 + P353-P304 + P340 + P310-P305 + P351 + P338 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Faceshields;full-face particle respirator type N100 (US);Gloves;respirator cartridge type N100 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter;type P3 (EN 143) respirator cartridges |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive; |
| Risk Phrases | R21/22;R34;R37 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45-S22-S27 |
| RIDADR | UN 2735 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| RTECS | MO1180000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 2921229000 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921229000 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921229000 hexamethylenediamine and its salts VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Fluorescence Imaging Assisted Photodynamic Therapy Using Photosensitizer-Linked Gold Quantum Clusters.
ACS Nano 9 , 5825-32, (2015) Fluorescence imaging assisted photodynamic therapy (PDT) is a viable two-in-one clinical tool for cancer treatment and follow-up. While the surface plasmon effect of gold nanorods and nanoparticles ha... |
|
|
Rapid and sensitive determination of diacetylpolyamines in human fingernail by ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry.
Eur. J. Mass Spectrom. (Chichester, Eng.) 20(6) , 477-86, (2015) A rapid and sensitive ultraperformance liquid chromatography coupled with electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry (UPLC-ESI-MS/MS) method has been developed and validated for quantitatively d... |
|
|
Protease-degradable electrospun fibrous hydrogels.
Nat. Commun. 6 , 6639, (2015) Electrospun nanofibres are promising in biomedical applications to replicate features of the natural extracellular matrix (ECM). However, nearly all electrospun scaffolds are either non-degradable or ... |
| 1,6-Diaminohexane |
| 1,6-Hexamethylenediamine |
| 1,6-Hexanediamine |
| EINECS 204-679-6 |
| Hexamethylenediamine |
| MFCD00008243 |
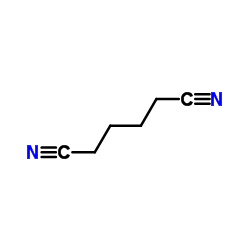 CAS#:111-69-3
CAS#:111-69-3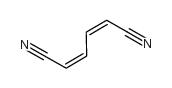 CAS#:1557-59-1
CAS#:1557-59-1 CAS#:2432-74-8
CAS#:2432-74-8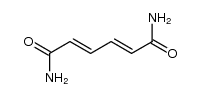 CAS#:5867-86-7
CAS#:5867-86-7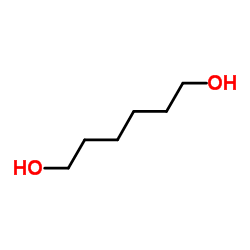 CAS#:629-11-8
CAS#:629-11-8 CAS#:5867-88-9
CAS#:5867-88-9 CAS#:1080571-11-4
CAS#:1080571-11-4 CAS#:111-49-9
CAS#:111-49-9 CAS#:1336-21-6
CAS#:1336-21-6 CAS#:10513-98-1
CAS#:10513-98-1![(2R,3R,4S,5R)-2-[6-[6-[[9-[(2R,3R,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]purin-6-yl]amino]hexylamino]purin-9-yl]-5-(hydroxymethyl)oxolane-3,4-diol structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/074/111863-61-7.png) CAS#:111863-61-7
CAS#:111863-61-7 CAS#:25079-94-1
CAS#:25079-94-1 CAS#:86013-63-0
CAS#:86013-63-0 CAS#:74-89-5
CAS#:74-89-5 CAS#:5586-70-9
CAS#:5586-70-9 CAS#:4856-87-5
CAS#:4856-87-5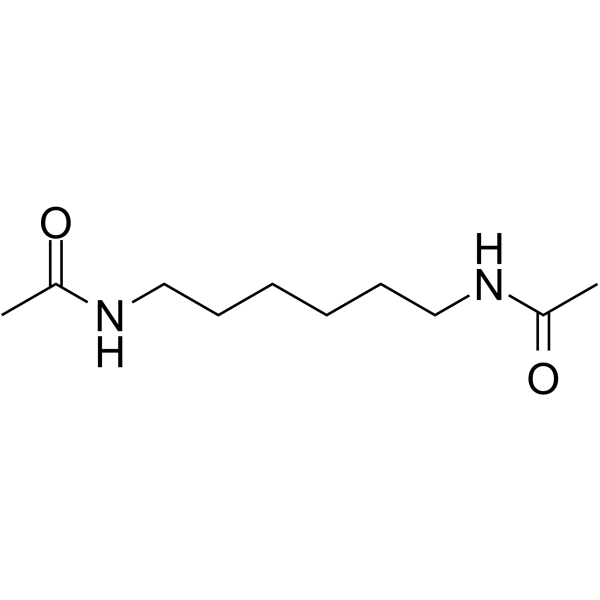 CAS#:3073-59-4
CAS#:3073-59-4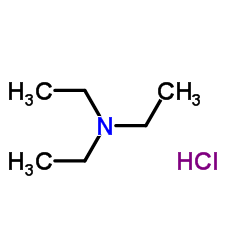 CAS#:554-68-7
CAS#:554-68-7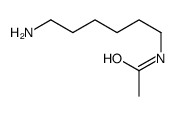 CAS#:49631-88-1
CAS#:49631-88-1
