Galactinol (hydrate)
Modify Date: 2025-11-10 06:24:11
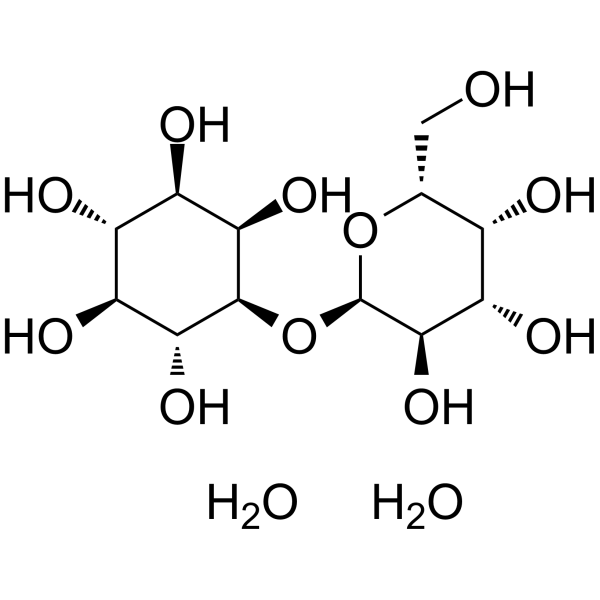
Galactinol (hydrate) structure
|
Common Name | Galactinol (hydrate) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1217474-91-3 | Molecular Weight | 378.327 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C12H26O13 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Galactinol (hydrate)Galactinol dihydrate is a marker for seed longevity. Galactinol dihydrate can scavenge hydroxyl radicals and protect plant cells from oxidative damage caused by MV treatment, salinity, or chilling[1]. |
| Name | Galactinol (hydrate) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Galactinol dihydrate is a marker for seed longevity. Galactinol dihydrate can scavenge hydroxyl radicals and protect plant cells from oxidative damage caused by MV treatment, salinity, or chilling[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
[1]. Vidigal DS, et, al. Galactinol as marker for seed longevity. Plant Sci. 2016 May;246:112-118. |
| Molecular Formula | C12H26O13 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 378.327 |
| Exact Mass | 378.137329 |
| 8665287 |
| α-D-Galactopyranoside, (1α,2α,3α,4β,5α,6β)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxycyclohexyl, hydrate (1:2) |
| EINECS 210-165-2 |
| Galactinol Dihydrate |
| (1S,2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2,3,4,5,6-Pentahydroxycyclohexyl α-D-galactopyranoside dihydrate |
| MFCD01631159 |