Indole
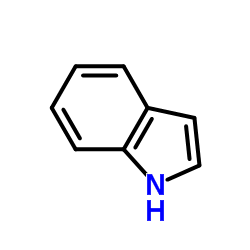
Indole structure
|
Common Name | Indole | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 120-72-9 | Molecular Weight | 117.148 | |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 253.0±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7N | Melting Point | 51-54 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 107.8±11.3 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | 1H-indole |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 1.1±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 253.0±9.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 51-54 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C8H7N |
| Molecular Weight | 117.148 |
| Flash Point | 107.8±11.3 °C |
| Exact Mass | 117.057846 |
| PSA | 15.79000 |
| LogP | 2.14 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.5 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.681 |
| InChIKey | SIKJAQJRHWYJAI-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | c1ccc2[nH]ccc2c1 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Stability | Stable, but may be light or air sensitive. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, iron and iron salts. |
| Water Solubility | 2.80 g/L (25 ºC) |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS06, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H311-H315-H318-H335-H400 |
| Precautionary Statements | P261-P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P312 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Faceshields;Gloves |
| Hazard Codes | Xn:Harmful |
| Risk Phrases | R21/22;R36 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S60-S61-S45-S36/37 |
| RIDADR | UN 2811 6.1/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 1 |
| RTECS | NL2450000 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 9 |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
| Precursor 0 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2933990090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2933990090. heterocyclic compounds with nitrogen hetero-atom(s) only. VAT:17.0%. Tax rebate rate:13.0%. . MFN tariff:6.5%. General tariff:20.0% |
|
Sequential electrochemical treatment of dairy wastewater using aluminum and DSA-type anodes.
Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 21(14) , 8573-84, (2014) Dairy wastewater is characterized by a high content of hardly biodegradable dissolved, colloidal, and suspended organic matter. This work firstly investigates the performance of two individual electro... |
|
|
The aryl hydrocarbon receptor-dependent disruption of contact inhibition in rat liver WB-F344 epithelial cells is linked with induction of survivin, but not with inhibition of apoptosis.
Toxicology 333 , 37-44, (2015) Inhibition of apoptosis by the ligands of the aryl hydrocarbon receptor (AhR) has been proposed to play a role in their tumor promoting effects on liver parenchymal cells. However, little is presently... |
|
|
Enhanced Photoreduction of Nitro-aromatic Compounds by Hydrated Electrons Derived from Indole on Natural Montmorillonite.
Environ. Sci. Technol. 49 , 7784-92, (2015) A new photoreduction pathway for nitro-aromatic compounds (NACs) and the underlying degradation mechanism are described. 1,3-Dinitrobenzene was reduced to 3-nitroaniline by the widely distributed arom... |
| 1H-Benzo[b]pyrrole |
| EINECS 204-420-7 |
| 2,3-Benzopyrrole |
| Indol |
| MFCD00005607 |
| Indole |
| UNII-8724FJW4M5 |
| 1H-Indole |
| 1-Azaindene |
| 2,3-Benzopyrole |
| Ketole |
| T56 BMJ |
| 1-Benzazole |
| benzazole |
| Benzo[b]pyrrole |
| Indole (8CI) |
| Benzopyrrole |
| 1H-Indole (9CI) |
 CAS#:108939-97-5
CAS#:108939-97-5 CAS#:108977-91-9
CAS#:108977-91-9 CAS#:106154-54-5
CAS#:106154-54-5 CAS#:109241-98-7
CAS#:109241-98-7![2-phenyl-5H-pyrazolo[3,4-c]quinolin-4-one structure](https://image.chemsrc.com/caspic/346/109740-09-2.png) CAS#:109740-09-2
CAS#:109740-09-2 CAS#:375-97-3
CAS#:375-97-3 CAS#:612-59-9
CAS#:612-59-9 CAS#:487-89-8
CAS#:487-89-8 CAS#:61-50-7
CAS#:61-50-7 CAS#:58494-59-0
CAS#:58494-59-0
