Lidocaine-d10 hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2025-08-21 14:29:30
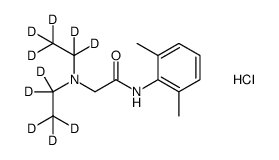
Lidocaine-d10 hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Lidocaine-d10 hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1189959-13-4 | Molecular Weight | 278.84800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C14H15ClD8N2O | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Lidocaine-d10 hydrochlorideLidocaine-d10 (Lignocaine-d10) hydrochloride is the deuterium labeled Lidocaine hydrochloride. Lidocaine hydrochloride (Lignocaine hydrochloride) inhibits sodium channels involving complex voltage and using dependence[1]. Lidocaine hydrochloride decreases growth, migration and invasion of gastric carcinoma cells via up-regulating miR-145 expression and further inactivation of MEK/ERK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Lidocaine hydrochloride is an amide derivative commonly used to anesthetize. hydrochloride is a a drug to treat ventricular arrhythmia and an effective tumor-inhibitor[2]. |
| Name | Lidocaine-d10 hydrochloride |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Lidocaine-d10 (Lignocaine-d10) hydrochloride is the deuterium labeled Lidocaine hydrochloride. Lidocaine hydrochloride (Lignocaine hydrochloride) inhibits sodium channels involving complex voltage and using dependence[1]. Lidocaine hydrochloride decreases growth, migration and invasion of gastric carcinoma cells via up-regulating miR-145 expression and further inactivation of MEK/ERK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Lidocaine hydrochloride is an amide derivative commonly used to anesthetize. hydrochloride is a a drug to treat ventricular arrhythmia and an effective tumor-inhibitor[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Stable heavy isotopes of hydrogen, carbon, and other elements have been incorporated into drug molecules, largely as tracers for quantitation during the drug development process. Deuteration has gained attention because of its potential to affect the pharmacokinetic and metabolic profiles of drugs[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C14H15ClD8N2O |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 278.84800 |
| Exact Mass | 278.20000 |
| PSA | 35.83000 |
| LogP | 4.03520 |
| 2-[bis(pentadeuterioethyl)amino]-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide hydrochloride |
| 2-(bis(perdeuterioethyl)amino)-N-(2,6-dimethylphenyl)acetamide hydrochloride |