Valecobulin
Modify Date: 2025-08-27 10:43:39
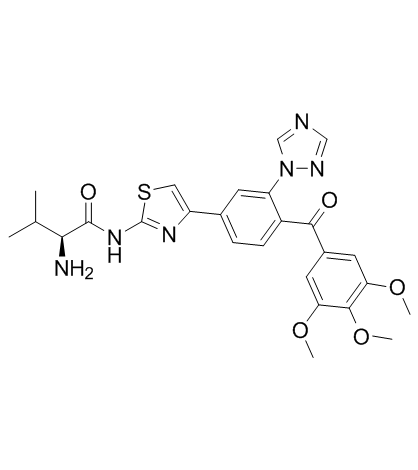
Valecobulin structure
|
Common Name | Valecobulin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1188371-47-2 | Molecular Weight | 536.60300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C26H28N6O5S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of ValecobulinValecobulin (CKD516), a valine prodrug of (S516) and a vascular disrupting agent (VDA), is a potent beta-tubulin polymerization inhibitor with marked antitumor activity against murine and human solid tumors[1][2]. |
| Name | (2S)-2-amino-3-methyl-N-[4-[3-(1,2,4-triazol-1-yl)-4-(3,4,5-trimethoxybenzoyl)phenyl]-1,3-thiazol-2-yl]butanamide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Valecobulin (CKD516), a valine prodrug of (S516) and a vascular disrupting agent (VDA), is a potent beta-tubulin polymerization inhibitor with marked antitumor activity against murine and human solid tumors[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Beta-tubulin polymerization[1]. |
| In Vivo | The size change of the tumor in VX2 liver tumor-bearing rabbits is significantly smaller in the Valecobulin (CKD516)( 5, 9, or 12 mg/m2, i.v.)- treated group than in control group[2]. Animal Model: VX2 liver tumor-bearing rabbits (Male New Zealand White rabbits weighing between 2.5 and 3.5 kg)[2]. Dosage: Dissolved in 5 mL of saline at a dose of 5, 9, or 12 mg/m2 of body surface area. Administration: Intravenous injection once. Result: The size change of the tumors was significantly smaller in the treated group than in control group. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C26H28N6O5S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 536.60300 |
| Exact Mass | 536.18400 |
| PSA | 175.21000 |
| LogP | 4.91920 |
| UNII-P48P97V001 |
| CKD-516 free base |