Dioctylamine

Dioctylamine structure
|
Common Name | Dioctylamine | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1120-48-5 | Molecular Weight | 241.456 | |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 | Boiling Point | 297.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C16H35N | Melting Point | 13-16 °C(lit.) | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 126.8±10.7 °C | |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
Signal Word | Danger | |
| Name | Dioctylamine |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 0.8±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 297.5±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Melting Point | 13-16 °C(lit.) |
| Molecular Formula | C16H35N |
| Molecular Weight | 241.456 |
| Flash Point | 126.8±10.7 °C |
| Exact Mass | 241.276947 |
| PSA | 12.03000 |
| LogP | 7.01 |
| Vapour density | 8.3 (vs air) |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±0.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.442 |
| Stability | Stable. Combustible. Incompatible with strong oxidizing agents, acids. |
| Water Solubility | immiscible |
| Symbol |



GHS05, GHS07, GHS09 |
|---|---|
| Signal Word | Danger |
| Hazard Statements | H302-H314-H410 |
| Precautionary Statements | P273-P280-P305 + P351 + P338-P310-P501 |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Faceshields;full-face respirator (US);Gloves;Goggles;multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US);type ABEK (EN14387) respirator filter |
| Hazard Codes | C:Corrosive;N:Dangerousfortheenvironment; |
| Risk Phrases | R34;R50/53 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36/37/39-S45-S60-S61-S29 |
| RIDADR | UN 2735 8/PG 3 |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
| Packaging Group | III |
| Hazard Class | 8 |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
| Precursor 9 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 10 | |
| HS Code | 2921199090 |
|---|---|
| Summary | 2921199090 other acyclic monoamines and their derivatives; salts thereof VAT:17.0% Tax rebate rate:9.0% Supervision conditions:none MFN tariff:6.5% General tariff:30.0% |
|
Compact and blinking-suppressed quantum dots for single-particle tracking in live cells.
J. Phys. Chem. B 118(49) , 14140-7, (2014) Quantum dots (QDs) offer distinct advantages over organic dyes and fluorescent proteins for biological imaging applications because of their brightness, photostability, and tunability. However, a majo... |
|
|
Probing charge transfer in a novel class of luminescent perovskite-based heterostructures composed of quantum dots bound to RE-activated CaTiO3 phosphors.
Nanoscale 8 , 2129-42, (2016) We report on the synthesis and structural characterization of novel semiconducting heterostructures composed of cadmium selenide (CdSe) quantum dots (QDs) attached onto the surfaces of novel high-surf... |
|
|
The Biological Effects of Bilirubin Photoisomers.
PLoS ONE 11 , e0148126, (2016) Although phototherapy was introduced as early as 1950's, the potential biological effects of bilirubin photoisomers (PI) generated during phototherapy remain unclear. The aim of our study was to isola... |
| Di-n-octylamine |
| RC5632 |
| EINECS 214-311-6 |
| n-octyl2-NH |
| MFCD00009557 |
| Dioctylamin |
| N-Octyloctan-1-amine |
| N,N-di-n-octylamine |
| di(n-octyl)amine |
| n-octyl-1-octanamin |
| 1-Octanamine, N-octyl- |
| N-Octyl-1-octanamine |
| N-n-Octyl-n-octylamine |
| DNOA |
| Dioctylamine |
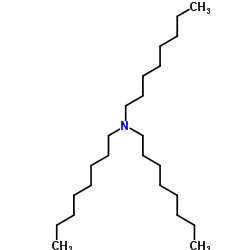 CAS#:1116-76-3
CAS#:1116-76-3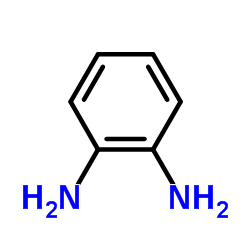 CAS#:95-54-5
CAS#:95-54-5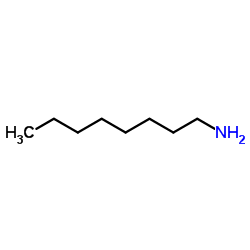 CAS#:111-86-4
CAS#:111-86-4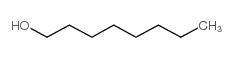 CAS#:111-87-5
CAS#:111-87-5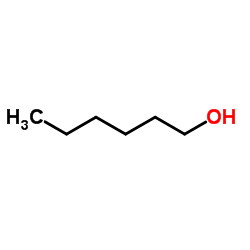 CAS#:111-27-3
CAS#:111-27-3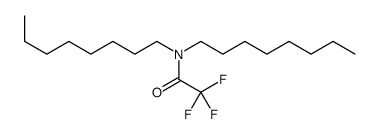 CAS#:14618-32-7
CAS#:14618-32-7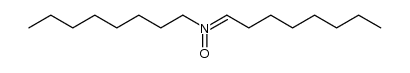 CAS#:339529-04-3
CAS#:339529-04-3 CAS#:4088-41-9
CAS#:4088-41-9 CAS#:10576-04-2
CAS#:10576-04-2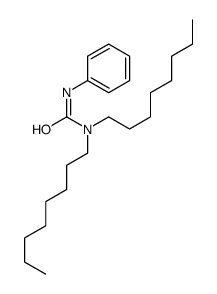 CAS#:144106-04-7
CAS#:144106-04-7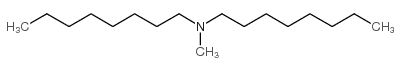 CAS#:4455-26-9
CAS#:4455-26-9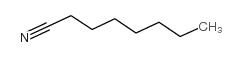 CAS#:124-12-9
CAS#:124-12-9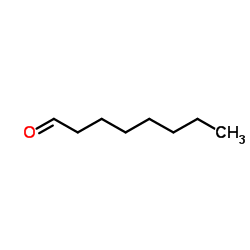 CAS#:124-13-0
CAS#:124-13-0 CAS#:25284-54-2
CAS#:25284-54-2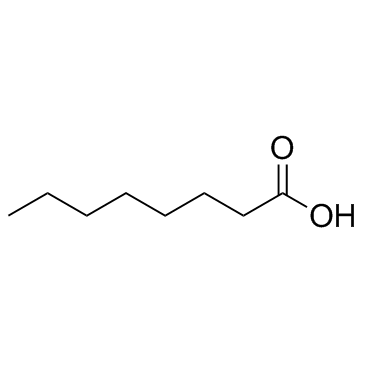 CAS#:124-07-2
CAS#:124-07-2 CAS#:42886-89-5
CAS#:42886-89-5 CAS#:76058-01-0
CAS#:76058-01-0
