Monazomycin
Modify Date: 2025-08-27 18:30:37
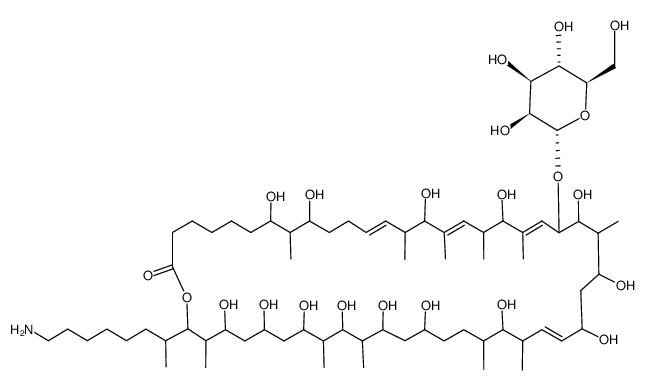
Monazomycin structure
|
Common Name | Monazomycin | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 11006-31-8 | Molecular Weight | 1364.82000 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C72H133NO22 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of MonazomycinMonazomycin is a polyene-like antibiotic produced by Streptomyces. Monazomycin molecular weight is about 1200[1]. |
| Name | monoazomycin |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Monazomycin is a polyene-like antibiotic produced by Streptomyces. Monazomycin molecular weight is about 1200[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | Monazomycin is an antibiotic produced by Streptomyces. Its molecular weight is about 1200, and is related to that of polyene antibiotics. Monazomycin has an amino group that gives a positive charge to the molecule at neutral pH. When monazomycin is added in micromolar amounts to one side of a bilayer, membrane conductance becomes strongly voltage-dependent. Monazomycin is present in the solution in the form of relatively hydrophilic clusters and is adsorbed as such on top of the lipid bilayer, penetration into the bilayer following a potential jump is assumed to be preceded by a potential-independent disaggregation of the adsorbed clusters into adsorbed monomers[1]. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C72H133NO22 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 1364.82000 |
| Exact Mass | 1363.93000 |
| PSA | 434.92000 |
| LogP | 4.19630 |
| MONAZOMYCIN |
| Monazomycin |