Cardiogenol C (hydrochloride)
Modify Date: 2024-01-12 16:38:54
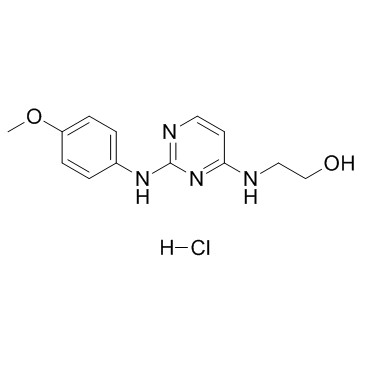
Cardiogenol C (hydrochloride) structure
|
Common Name | Cardiogenol C (hydrochloride) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1049741-55-0 | Molecular Weight | 296.75300 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C13H17ClN4O2 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Cardiogenol C (hydrochloride)Cardiogenol C hydrochloride is a cell-permeable pyrimidine compound which potently induces the differentiation of ESCs into cardiomyocytes (EC50= 100 nM).IC50 value: 100 nM (EC50)Target:in vitro: Cardiogenol C hydrochloride is a cardiomyogenesis inducer in embryonic stem cells. Cardiogenol C induces the differentiation of myosin heavy chain-positive cardiomyocytes from embryonic stem cells with an EC50 value of 0.1 μM; about 90% of embryonic stem cells treated with 0.25 μM of Cardiogenol C express the cardiac muscle cell specific transcription factors GATA-4, MEF2, and Nkx2.5 and display the characteristic beating behavior of differentiated cardiomyocytes. Cardiogenol C (a diaminopyrimidine) induces cardiac differentiation in P19 and in P19Cl6 cells. [1] Cardiogenol C could activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling to induce cardiogenesis. Cardiogenol C-treatment significantly decreased HBPCs proliferation. Cardiogenol C was able to induce HBPCs to transdifferentiate into cardiomyocyte-like cells.[2] |
| Name | 2-({2-[(4-Methoxyphenyl)amino]-4-pyrimidinyl}amino)ethanol hydroc hloride (1:1) |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Description | Cardiogenol C hydrochloride is a cell-permeable pyrimidine compound which potently induces the differentiation of ESCs into cardiomyocytes (EC50= 100 nM).IC50 value: 100 nM (EC50)Target:in vitro: Cardiogenol C hydrochloride is a cardiomyogenesis inducer in embryonic stem cells. Cardiogenol C induces the differentiation of myosin heavy chain-positive cardiomyocytes from embryonic stem cells with an EC50 value of 0.1 μM; about 90% of embryonic stem cells treated with 0.25 μM of Cardiogenol C express the cardiac muscle cell specific transcription factors GATA-4, MEF2, and Nkx2.5 and display the characteristic beating behavior of differentiated cardiomyocytes. Cardiogenol C (a diaminopyrimidine) induces cardiac differentiation in P19 and in P19Cl6 cells. [1] Cardiogenol C could activate Wnt/β-catenin signaling to induce cardiogenesis. Cardiogenol C-treatment significantly decreased HBPCs proliferation. Cardiogenol C was able to induce HBPCs to transdifferentiate into cardiomyocyte-like cells.[2] |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C13H17ClN4O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 296.75300 |
| Exact Mass | 296.10400 |
| PSA | 82.53000 |
| LogP | 1.92990 |
| Storage condition | -20℃ |
| Combretastatin A4 |
| Cardiogenol C,Hydrochloride |
| Cardiogenol C (hydrochloride) |