Diadenosine pentaphosphate pentaammonium
Modify Date: 2024-01-31 18:05:59
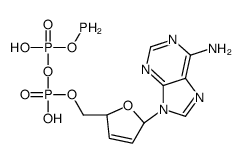
Diadenosine pentaphosphate pentaammonium structure
|
Common Name | Diadenosine pentaphosphate pentaammonium | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 102783-61-9 | Molecular Weight | 425.16800 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | 1394.9ºC at 760 mmHg | |
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N5O8P3 | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | USA | Flash Point | 797.4ºC | |
Use of Diadenosine pentaphosphate pentaammoniumDiadenosine pentaphosphate pentaammonium is an endogenous vasoactive purine dinucleotide which has been isolated from thrombocytes. Diadenosine polyphosphates (ApnA, n=2–7) have been identified as constituents of secretory vesicles such as in platelets, chromaffin cells, Torpedo synaptic terminals and brain synaptosomes[1][2]. |
| Name | [[(2S,5R)-5-(6-aminopurin-9-yl)-2,5-dihydrofuran-2-yl]methoxy-hydroxyphosphoryl] phosphanyl hydrogen phosphate |
|---|
| Description | Diadenosine pentaphosphate pentaammonium is an endogenous vasoactive purine dinucleotide which has been isolated from thrombocytes. Diadenosine polyphosphates (ApnA, n=2–7) have been identified as constituents of secretory vesicles such as in platelets, chromaffin cells, Torpedo synaptic terminals and brain synaptosomes[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Human Endogenous Metabolite |
| References |
| Boiling Point | 1394.9ºC at 760 mmHg |
|---|---|
| Molecular Formula | C10H14N5O8P3 |
| Molecular Weight | 425.16800 |
| Flash Point | 797.4ºC |
| Exact Mass | 425.00600 |
| PSA | 214.35000 |
| LogP | 1.48400 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0mmHg at 25°C |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|---|