oxosilylene

oxosilylene structure
|
Common Name | oxosilylene | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 10097-28-6 | Molecular Weight | 44.085 | |
| Density | 2.13 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) | Boiling Point | 1880°C | |
| Molecular Formula | OSi | Melting Point | 1870 °C | |
| MSDS | Chinese USA | Flash Point | 1880°C | |
| Name | silicon monoxide |
|---|---|
| Synonym | More Synonyms |
| Density | 2.13 g/mL at 25 °C(lit.) |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 1880°C |
| Melting Point | 1870 °C |
| Molecular Formula | OSi |
| Molecular Weight | 44.085 |
| Flash Point | 1880°C |
| Exact Mass | 43.971840 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.9800 |
| InChIKey | LIVNPJMFVYWSIS-UHFFFAOYSA-N |
| SMILES | O=[Si] |
| Stability | Stable. |
| Personal Protective Equipment | dust mask type N95 (US);Eyeshields;Gloves |
|---|---|
| Hazard Codes | Xi:Irritant; |
| Risk Phrases | R36/37/38 |
| Safety Phrases | S26-S36 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |
|
~% 
oxosilylene CAS#:10097-28-6 |
| Literature: Journal of the American Chemical Society, , vol. 111, # 13 p. 4578 - 4582 |
|
~% 
oxosilylene CAS#:10097-28-6 |
| Literature: Journal of Chemical Physics, , vol. 110, # 8 p. 3769 - 3772 |
|
~% 
oxosilylene CAS#:10097-28-6 |
| Literature: Chemical Physics Letters, , vol. 355, # 1-2 p. 31 - 36 |
|
~% 
oxosilylene CAS#:10097-28-6 |
| Literature: Chemical Physics, , vol. 100, p. 133 - 152 |
|
~% 
oxosilylene CAS#:10097-28-6 |
| Literature: Chemical Physics, , vol. 100, p. 153 - 170 |
|
~% 
oxosilylene CAS#:10097-28-6 |
| Literature: Zeitschrift fuer Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie, , vol. 460, p. 37 - 50 |
|
~% 
oxosilylene CAS#:10097-28-6 |
| Literature: Journal of Physical Chemistry, , vol. 100, # 44 p. 17501 - 17506 |
|
~% 
oxosilylene CAS#:10097-28-6 |
| Literature: Surface Science, , vol. 154, p. 347 - 356 |
|
Asymmetric fluorination of alpha-aryl acetic acid derivatives with the catalytic system NiCl2-Binap/R3SiOTf/2,6-lutidine.
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 46(28) , 5435-9, (2007)
|
|
|
How to make the ionic Si-O bond more covalent and the Si-O-Si linkage a better acceptor for hydrogen bonding.
Inorg. Chem. 48(10) , 4384-93, (2009) Variation of a bond angle can tune the reactivity of a chemical compound. To exemplify this concept, the nature of the siloxane linkage (Si-O-Si), the most abundant chemical bond in the earth's crust,... |
|
|
Silicon oxide nanoparticles reveal the origin of silicate grains in circumstellar environments.
Nano Lett. 6(6) , 1190-5, (2006) A synergistic effort combining experiments in beams and first principles theoretical investigations is used to propose mechanisms that could lead to the formation of silicates and nanoparticles with s... |
| Silicon Monoxide SiO |
| Monox |
| silicon oxide powder |
| Silylene,oxo |
| MFCD00151536 |
| oxosilylene |
| silylene, oxo- |
| Silicon monoxide |
| SILICON (II) OXIDE |
| Dihydrido(oxonio)silicate(1-) |
| oxo-silylen |
| SILICON OXIDE,MONO |
| Silicon oxide |
| SiO |
| Silicate(1-), dihydrooxonio- |
| EINECS 233-232-8 |



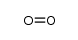

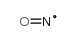

 CAS#:126807-09-8
CAS#:126807-09-8
