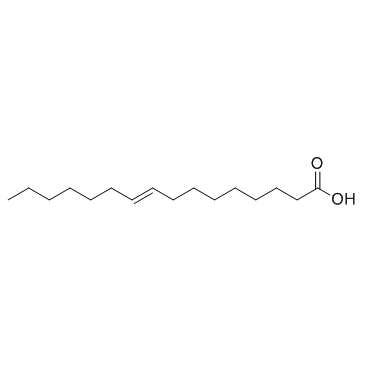
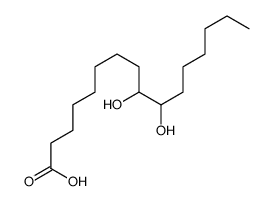
10030-73-6
| Name | palmitelaidic acid |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Palmitelaidic acid
trans-9-Hexadecenoic acid (9E)-9-Hexadecenoic acid (E)-Palmitoleic acid trans-9-palmitoleic acid trans-palmitoleic acid trans-Hexadec-9-enoic acid 9-trans-Hexadecenoic acid (9E)-hexadec-9-enoic acid cis-9hexadecenoic acid |
| Description | Palmitelaidic acid is the trans isomer of palmitoleic acid. Palmitoleic acid is one of the most abundant fatty acids in serum and tissue. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
AMPK PPARα Glucokinase |
| In Vitro | The monounsaturated fatty acid palmitoleate (palmitoleic acid) is one of the most abundant fatty acids in serum and tissues, particularly adipose tissue and liver. Its endogenous production by stearoyl-CoA desaturase 1 gives rise to its cis isoform, cis-palmitoleate. Palmitoleic acid has been correlated with multiple cardiometabolic risk factors, including high blood pressure, total cholesterol, TGs, apoA-I, apoB, and endothelial dysfunction[1]. |
| In Vivo | Palmitoleic acid promotes a faster uptake of glucose in the body, associated with higher insulin concentration. Palmitoleic acid increases the phosphorylation of AMPK, up-regulates glucokinase and down-regulates SREBP-1. Regarding AMPK downstream, palmitoleic acid increases the production of FGF-21 and stimulates the expression of PPARα[2]. Palmitoleic acid reduces body weight increase, ameliorates the development of hyperglycemia and hypertriglyceridemia, and improves insulin sensitivity. Furthermore, palmitoleic acid down-regulates mRNA expressions of proinflammatory adipocytokine genes (TNFα and resistin) in white adipose tissue and lipogenic genes (SREBP-1, FAS, and SCD-1) in liver[3]. |
| Animal Admin | Mice: Male C57BL/6J wild type and PPARα-KO mice are fed a high-fat diet or a standard diet for 12 weeks. In the last two weeks, the HF-fed mice are treated daily with oleic acid (300 mg/kg of body weight) or palmitoleic acid (00 mg/kg of body weight) by oral gavage. After 12 weeks, the mice are fasted for 6 h, injected with insulin or PBS vehicle. Blood and liver samples are collected and stored for the further analysis of RNA and protein expression[2]. |
| References |
[1]. Frigolet ME, et al. The Role of the Novel Lipokine Palmitoleic Acid in Health and Disease. |
| Density | 0.9±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 363.6±0.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C16H30O2 |
| Molecular Weight | 254.408 |
| Flash Point | 239.2±14.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 254.224579 |
| PSA | 37.30000 |
| LogP | 6.64 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.466 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 1 | |