646530-37-2
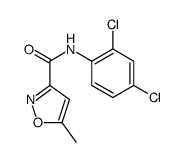
| Name | N-(2,4-dichlorophenyl)-5-methyl-1,2-oxazole-3-carboxamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms | UTL-5g |
| Description | UTL-5g (GBL-5g), an anti-inflammatory TNF-α inhibitor, has chemoprotective and liver radioprotective effects. UTL-5g lowers hepatotoxicity, nephrotoxicity, and myelotoxicity induced by Cisplatin through TNF-α inhibition among other factors[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | RAW 264.7 macrophages are transfected with the respective reporter assay plasmids, pretreated with UTL-5g at 1, 10 or 50 µM for 60 min and then challenged with 100 ng/ml LPS. After a 16 h incubation, transcription factor activity is measured. Transcription factors that shows a UTL-5g dose-dependent decrease in activity in two experiments are categorized as being disrupted by UTL-5g. |
| In Vivo | UTL-5g (GBL-5g) lowers levels of TGF-β and TNF-α elevated by lung irradiation[1]. UTL-5g (60 mg/kg; p.o.; daily for 4 days) shows positive effects in increasing the survival rates and extending the survival times[3]. Animal Model: C57BL/6, male mice (8-10 weeks)[1] Dosage: 15, 30, and 60 mg/kg Administration: I.p.; before irradiation, daily x 5 Result: Blood levels of TGF-β were lowered. Animal Model: BDF1 female mice[3] Dosage: P.o.; daily for 4 days Administration: 60 mg/kg (30 min before i.p. injection of Cisplatin at 10, 15, and 20 mg/kg respectively on Day 0) Result: Increased the survival rate and delayed the time to death for mice treated with 150% of the maximum tolerated dose (MTD) of Cisplatin (15 mg/kg). At 200% of the MTD of Cisplatin (20 mg/kg), treatment of UTL-5g increased the survival rate and delayed the time to death. |
| References |
[1]. Stephen Brown, et al. UTL-5g Lowers Levels of TGF-β and TNF-α Elevated by Lung Irradiation |
| Molecular Formula | C11H8Cl2N2O2 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 271.09900 |
| Exact Mass | 269.99600 |
| PSA | 55.13000 |
| LogP | 3.61510 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|