128470-16-6
| Name | arbutamine |
|---|---|
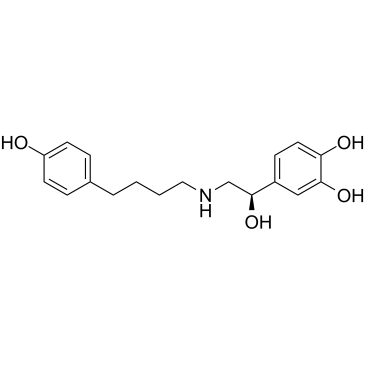
| Synonyms | 4-[(1R)-1-Hydroxy-2-{[4-(4-hydroxyphenyl)butyl]amino}ethyl]-1,2-b enzenediol |
| Description | Arbutamine is a short-acting synthetic potent nonselective β-adrenoceptor agonist that increases heart rate, cardiac contractility, and systolic blood pressure[1]. Arbutamine is a catecholamine for a pharmacological cardiac stress agen[2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
β-adrenoceptor[1] |
| In Vivo | Arbutamine (i.v.; 5, 10, 50, 100, and 250 ng/kg/min) increases mean heart rate, peak positive left ventricular pressure and its first time-derivative, and normal-zone myocardial thickening in 8 open-chest dogs (mean weight, 26.91 kg). |
| References |
| Density | 1.262g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 578.3ºC at 760mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C18H23NO4 |
| Molecular Weight | 317.38000 |
| Flash Point | 195.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 317.16300 |
| PSA | 92.95000 |
| LogP | 2.84020 |