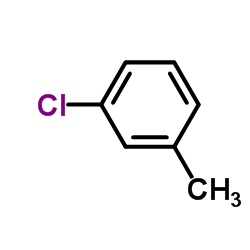
671-88-5
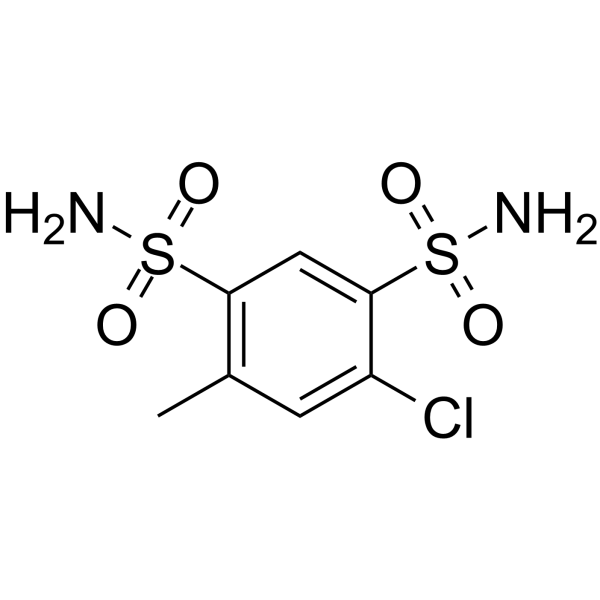
| Name | 4-chloro-6-methylbenzene-1,3-disulfonamide |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Diuroblitz
5-chloro-toluene-2,4-disulfonic acid diamide Edemil Desamide Tolclotidum Disulphamide 5-Chlor-toluol-2,4-disulfonsaeure-diamid Toluidrin 6-Chlor-4-methyl-benzol-1,3-disulfonsaeurediamid 5-Chlor-toluol-2,4-disulfonamid Disamide Toluren Ethacrynic acid Disulfamide Fisiuretik |
| Description | Disulfamide, an orally active diuretic, is a carbonic anhydrase inhibitor with the IC50 value of 0.07 μM. Disulfamide leads to diuresis by inhibiting carbonic anhydrase and preventing the reabsorption of sodium and bicarbonate in the proximal tubule[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 0.07 μM (carbonic anhydrase)[1] |
| In Vivo | Disulfamide (intraperitoneal injection, 200 mg/kg, once) has potential blood glucose raising properties in male Wistar rats[2]. Animal Model: Male Wistar rats weighing between 200-300 g[2] Dosage: 200 mg/kg Administration: Intraperitoneal injection; once Result: Resulted in elevated blood sugar levels from an initial blood glucose concentration of 143.1 mg/100 mL to a one hour later final concentration of 194.6 mg/100 mL, an increase of 36%. |
| References |
[2]. J M Foy, et al. Acute diuretic induced hyperglycaemia in rats. Life Sci. 1967 May 1;6(9):897-902. |
| Density | 1.621g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 549.4ºC at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C7H9ClN2O4S2 |
| Molecular Weight | 284.74000 |
| Flash Point | 286.1ºC |
| Exact Mass | 283.96900 |
| PSA | 137.08000 |
| LogP | 3.50540 |
| Index of Refraction | 1.612 |
CHEMICAL IDENTIFICATION
HEALTH HAZARD DATAACUTE TOXICITY DATA
|
|
~% 
671-88-5 |
| Literature: de Stevens et al. Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, 1959 , vol. 1, p. 565,573 |
|
~% 
671-88-5 |
| Literature: de Stevens et al. Journal of Medicinal and Pharmaceutical Chemistry, 1959 , vol. 1, p. 565,573 |
| Precursor 1 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |