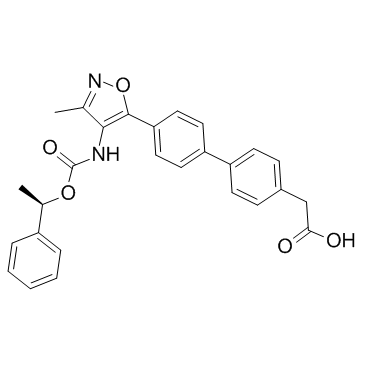
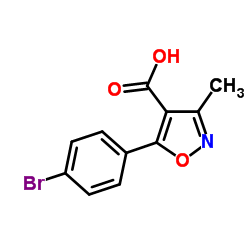
1345614-59-6
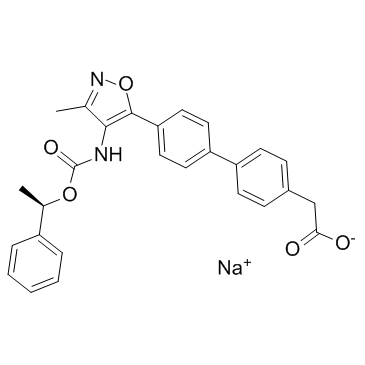
| Name | sodium,2-[4-[4-[3-methyl-4-[[(1R)-1-phenylethoxy]carbonylamino]-1,2-oxazol-5-yl]phenyl]phenyl]acetate |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
AM095||AM-095
CS-1118 sodium (4'-(3-methyl-4-((R)-1-phenyl-ethoxycarbonylamino)-isoxazol-5-yl)-biphenyl-4-yl)-acetic acid AM-095 AM095 |
| Description | AM095 is a selective LPA1 receptor antagonist. The IC50 for AM095 antagonism of LPA-induced calcium flux of human or mouse LPA1-transfected CHO cells is 0.025 and 0.023 μM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
LPA1 receptor[1] |
| In Vitro | AM095 is a potent LPA1 receptor antagonist because it inhibits GTPγS binding to Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cell membranes overexpressing recombinant human or mouse LPA1 with IC50 values of 0.98 and 0.73 μM, respectively. AM095 inhibits LPA-driven chemotaxis of CHO cells overexpressing mouse LPA1 (IC50=778 nM) and human A2058 melanoma cells (IC50=233 nM). The IC50 of AM095 in the human LPA1 GTPγS binding assay is comparable with that of our previously published compound AM966 (IC50=0.98±0.17 μM) and the Debio-0719 compound (IC50=0.60±0.04 μM)[1]. AM095 inhibits the LPA-induced calcium flux of CHO cells stably transfected with human or mouse LPA1. The IC50 for AM095 antagonism of LPA-induced calcium flux of human or mouse LPA1-transfected CHO cells is 0.025 and 0.023 μM, respectively[2]. |
| In Vivo | AM095 has high oral bioavailability and a moderate half-life and is well tolerated at the doses tested in rats and dogs after oral and intravenous dosing. After oral (10 mg/kg) dosing in rats, AM095 plasma concentrations peaked at 2 h with a Cmax of 41 μM, thereafter decreasing to 10 nM by 24 h. After intravenous (2 mg/kg) dosing, a Cmax of 12 μM is observed within 15 min, which also decreased to approximately 10 nM by 24 h, yielding a t1/2 of 1.79 h. In dogs, a single oral dose of 5 mg/kg yielded a peak plasma concentration of 21 μM within 15 min of dosing, which then decreased to 10 nM by 24 h. In contrast, an intravenous dose of 2 mg/kg resulted in a Cmax of 11 μM within 15 min and decreased to 15 nM by 8 h, yielding a t1/2 of 1.5 h[1]. |
| Kinase Assay | Known amounts of AM095 (diluted in DMSO) or vehicle (DMSO) are added to 25 to 40 μg of hLPA1/CHO or mLPA1/CHO membranes and 0.1 nM [35S]-GTPγS in buffer (50 mM HEPES, 0.1 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2, 50 μg/mL saponin, pH 7.5) containing 0.2% fatty acid-free human serum albumin and 5 μM GDP. To test for LPA1 antagonist activity, the ability of AM095 to inhibit GTPγS binding stimulated by 900 nM LPA (18:1) is measured. Alternatively, to test for agonist effects, the ability of AM095 to stimulate GTPγS binding in the absence of LPA is measured. Reactions are incubated for 30 min at 30°C, before harvesting membranes onto glass filter binding plates (UniFilter GF/B) and washing three times with cold buffer containing 50 mM HEPES, pH 7.4, 100 mM NaCl, 10 mM MgCl2 using a Brandel 96-tip cell harvester. Plates are dried and then cpm are evaluated by using a Packard TopCount NXT microplate scintillation counter[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats[1] Male Sprague-Dawley rats with surgically implanted jugular vein catheters (250-300 g) are used. In all studies, animals are fasted 15 to 24 h before dosing. For rats, AM095 is administered intraveneously at a dose of 2 mg/kg in 0.9% saline given as a 1 mL/kg bolus injection into the jugular vein. To determine oral exposure, AM095 is administered as a solution in 0.5% methylcellulose via an oral gavage at a dose of 10 mg/kg in a volume of 3 mL/kg. Blood samples (approximately 300 μL of total blood) are taken from each rat via the jugular vein catheter at times up to 24 h postdose (10-11 samples per animal) in potassium EDTA tubes. After each sampling, the catheter is flushed with an equivalent volume of saline. Plasma samples, prepared by centrifugation of whole blood, are stored frozen (−80°C) before analysis. AM095 is dosed intravenously at 2 mg/kg and orally at 5 mg/kg to male beagle dogs (n=3). Plasma samples are collected and analyzed for AM095 concentration by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry. Mice[2] C57Bl/6 mice are administered the selective LPA1 antagonist AM095 by oral gavage (30 mg/kg) at time 0 and 8 h, and blood is collected by cardiac puncture under anesthesia in sodium EDTA tubes at 0, 4, 8, 9, 12 and 24 h. Plasma samples are stored at −40°C prior to analysis of AM095 concentrations by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS). Known amounts of AM095 are added to thawed mouse plasma to yield a concentration range from 0.8 to 4,000 ng/mL. Plasma samples are precipitated using acetonitrile containing the internal standard buspirone. The analyte mixture (10 μL) is injected using a Leap PAL autosampler. Calibration curves are constructed by plotting the peak-area ratio of analyzed peaks against known concentrations. The lower limit of quantitation is 1 ng/mL. The data are subjected to linear regression analysis with 1/x2 weighting. The pharmacokinetic parameters of AM095 are calculated by non-compartmental analysis using WinNonlin Professional. Cmax and time to Cmax (Tmax) are obtained directly from the measured data. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C27H23N2NaO5 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 478.47200 |
| Exact Mass | 478.15000 |
| PSA | 107.98000 |
| LogP | 4.93270 |
| Storage condition | -20°C |
|
~% 
1345614-59-6 |
| Literature: WO2011/159550 A2, ; Page/Page column 85-86 ; WO 2011/159550 A2 |
|
~% 
1345614-59-6 |
| Literature: WO2011/159550 A2, ; WO 2011/159550 A2 |
|
~% 
1345614-59-6 |
| Literature: WO2011/159550 A2, ; WO 2011/159550 A2 |
|
~% 
1345614-59-6 |
| Literature: WO2011/159550 A2, ; WO 2011/159550 A2 |
|
~% 
1345614-59-6 |
| Literature: WO2011/159550 A2, ; WO 2011/159550 A2 |
|
~% 
1345614-59-6 |
| Literature: WO2011/159550 A2, ; WO 2011/159550 A2 |
| Precursor 6 | |
|---|---|
| DownStream 0 | |