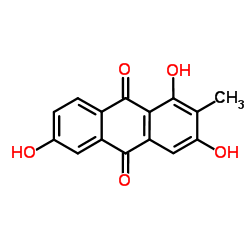
87686-86-0
| Name | 6-Hydroxyrubiadin |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
1,3,6-Trihydroxy-2-methyl-9,10-anthraquinone
1,3,6-trihydroxy-2-methylanthracene-9,10-dione 2-Methyl-1,3,6-trihydroxyanthraquinone |
| Description | 6-Hydroxyrubiadin, a natural anthraquinone, may be a potential therapeutic candidate for the treatment of inflammation and inflammatory diseases[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vitro | 6-hydroxyrubiadin suppresses lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced nuclear factor-kappa B activation as well as the phosphorylation of c-Jun N-terminal kinase in RAW 264.7 macrophages[1]. 6-hydroxyrubiadin inhibited the expression of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-a, interleukin (IL)-1b and IL-6 in phorbol myristate acetate (PMA)-primed U937 and RAW 264.7cells[1]. |
| In Vivo | 6-hydroxyrubiadin can reduce the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and ameliorate acute lung injury (ALI) in a mouse model[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 558.7±19.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C15H10O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 270.237 |
| Flash Point | 305.7±18.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 270.052826 |
| PSA | 94.83000 |
| LogP | 4.42 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.6 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.745 |
| Hazard Codes | Xi |
|---|