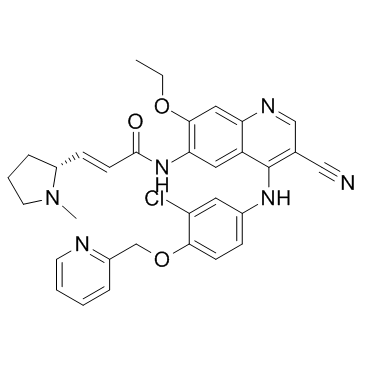
1269662-73-8
| Name | Pyrotinib |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
2-Propenamide, N-[4-[[3-chloro-4-(2-pyridinylmethoxy)phenyl]amino]-3-cyano-7-ethoxy-6-quinolinyl]-3-[(2R)-1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl]-, (2E)-
PYROTINIB (2E)-N-(4-{[3-Chloro-4-(2-pyridinylmethoxy)phenyl]amino}-3-cyano-7-ethoxy-6-quinolinyl)-3-[(2R)-1-methyl-2-pyrrolidinyl]acrylamide |
| Description | Pyrotinib (SHR-1258) is a potent and selective EGFR/HER2 dual inhibitor with IC50s of 13 and 38 nM, respectively. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
EGFR:13 nM (IC50) HER2:38 nM (IC50) |
| In Vitro | Pyrotinib has high potency in HER2-dependent cell lines (BT474, SK-OV-3), while showing much weaker inhibition in the HER2 negative cell line (MDA-MB-231). It inhibits BT474 and SK-OV-3Pyrotinib cells with IC50s of 5.1 and 43 nM, respectively. Pyrotinib displays high selectivity as HKI-272 when tested in a panel of different kinases such as KDR, c-Kit, PDGFRβ, c-Src and C-Met (c-Src with an IC50 of 790 nM, and others over 3000 nM)[1]. |
| In Vivo | Pyrotinib has acceptable bioavailability of 20.6%, 43.5% and 13.5% in nude mice, rats and dogs, respectively. Pyrotinib has favorable drug-like physicochemical properties and shows relatively higher oral exposure in human subjects with a much longer half life than that of preclinical animal species such as mouse, rat and dog. The TGI % (tumor growth inhibition) of Pyrotinib on day 21 is 109%, 157%, 159% at the doses of 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg, 20 mg/kg respectively. Pyrotinib in SK-OV-3 ovarian xenograft model shows TGI% on day 21 of 2%, 12%, 83% at the doses of 2.5 mg/kg, 5 mg/kg, 10 mg/kg respectively), which further confirms its robust in vivo antitumor efficacy at 10 mg/kg[1]. |
| Cell Assay | Cancer cells (A431, SK-BR-3 and NCI-N87) are treated with a series of concentrations of Pyrotinib for 72 hours. Cell proliferation is determined by a sulforhodamine B (SRB) method. The IC50 values are calculated by the data of inhibition rates of serial concentrations of test compounds[1]. |
| Animal Admin | Rats: Test compounds (include Pyrotinib) are administrated in both intravenous (i.v.) and intragastric (i.g.) for mice to obtain their bioavailability. Plasma samples of nude mice is collected at pre-dose and 0.083, 0.25, 0.5, 1, 2, 4, 6, 8, 12, 24 h after the IV administration[1]. Mice: In vivo efficacy studies are performed on BALB/Ca-nude mice (6 to 7 weeks, female) from SLAC. Nude mice are hypodermic inoculated BT-474 human breast cancer cell or SK-OV-3 ovarian cancer cell. After tumor grows to 150-250 mm3, mice are randomly divided into groups and dosed with Pyrotinib (2.5, 5, 10, 20 mg/kg) once daily. The volume of tumors and the weight of the mice are measured and recorded for 2-3 times per week[1]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.4±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 775.5±60.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C32H31ClN6O3 |
| Molecular Weight | 583.080 |
| Flash Point | 422.8±32.9 °C |
| Exact Mass | 582.214600 |
| LogP | 5.64 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±2.7 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.677 |
| Storage condition | 2-8℃ |