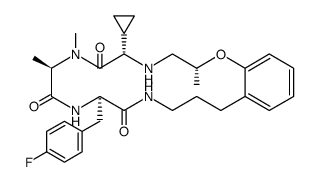
842131-33-3
| Name | D-Phenylalanine, (2S)-N-[(2R)-2-[2-(3-aminopropyl)phenoxy]propyl]-2-cyclopropylglycyl-N-methyl-D-alanyl-4-fluoro-, (3→1)-lactam |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Ulimorelin
TZP 101 |
| Description | Ulimorelin (TZP-101) is a ghrelin receptor (GRLN) agonist with an EC50 of 29 nM and a Ki of 16 nM. Ulimorelin is a prokinetic agent and causes vasorelaxation through competitive antagonist action at α1-adrenoceptors. Ulimorelin stimulates intestinal motility and is used for malnutrition[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| In Vivo | Ulimorelin (TZP-101; 0.3-5 mg/kg; i.v.) causes a dose dependent increase in the numbers and amplitudes of phasic pressure waves recorded from the colorectum[1]. Ulimorelin (1, 3, 5 mg/kg; i.v.) causes a substantial and prolonged (~1 h) increase in colorectal propulsive activity and expulsion of colonic contents[1]. Ulimorelin (p.o.; 8 mg/kg) has a Cmax of 0.39 μM and a AUC of 82 μM•min for rats. Ulimorelin (i.v.; 2 mg/kg) has a T1/2 of 50 mins, a CL of 24 mL/min/kg, and a Vss of 1.7 L/kg for rats[3]. Animal Model: Male Sprague-Dawley rats[1] Dosage: 0.3, 1, 3, 5 mg/kg Administration: i.v. Result: Caused a dose dependent increase in the numbers and amplitudes of phasic pressure waves recorded from the colorectum. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C30H39FN4O4 |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 538.65300 |
| Exact Mass | 538.29600 |
| PSA | 99.77000 |
| LogP | 3.52230 |