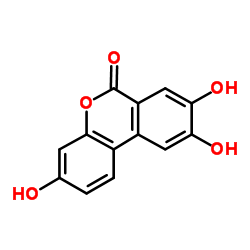
165393-06-6
| Name | Urolithin C |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Urolithin C
Uro C 3,8,9-thihydroxy-6H-benzo[c]chromen-6-one 3,8,9-Thihydroxybenzo[c]chromen-6-one 3,8,9-Trihydroxy-6H-benzo[c]chromen-6-one 3,8,9-trihydroxy-6H-dibenzo[b,d]pyran-6-one |
| Description | Urolithin C, a gut-microbial metabolite of Ellagic acid, is a glucose-dependent activator of insulin secretion. Urolithin C is a L-type Ca2+ channel opener and enhances Ca2+ influx. Urolithin C induces cell apoptosis through a mitochondria-mediated pathway and also stimulates reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation[1][2]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
Insulin secretion[1] L-type Ca2+ channel[1] Reactive oxygen species (ROS)[2] Apoptosis[2] |
| In Vitro | Urolithin C (20-100 μM; 1 hour; INS-1 cells) treatment enhances glucose-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) activation in INS-1 β-cells[1]. Urolithin C significantly inhibits the proliferation of PC12 cells. Urolithin C treatment actively increases the lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) release and lipid peroxidation malondialdehyde (MDA), stimulates reactive oxygen species (ROS) formation and mitochondrial membrane depolarization, and caused calcium dyshomeostasis[2]. Urolithin C treatment induces apoptosis and S phase cell cycle arrest[2]. Western Blot Analysis[1] Cell Line: INS-1 cells Concentration: 20 μM, 100 μM Incubation Time: 1 hour Result: Enhanced glucose-induced extracellular signal-regulated kinases 1/2 (ERK1/2) activation. |
| In Vivo | The pharmacokinetics of Urolithin C (10 mg/kg; intraperitoneal administration) in male Wistar rat (140-160 g) are studied. The half-life of the terminal part is 11.3 h and the total clearance (CL/F) is 3.41 L/h/kg. The initial volume of distribution (V1/F) and the steady-state volume of distribution (Vss/F) are 0.831 L/kg and 55.6 L/kg, respectively[3]. |
| References |
| Density | 1.6±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 605.4±55.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C13H8O5 |
| Molecular Weight | 244.200 |
| Flash Point | 243.6±25.0 °C |
| Exact Mass | 244.037170 |
| PSA | 90.90000 |
| LogP | 1.88 |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.0±1.8 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.758 |