9013-18-7
| Name | Acyl-coenzyme A synthetase |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Fatty acid CoA ligase
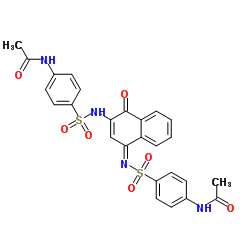
Acyl-CoA ligase N,N'-[(4-Oxo-3-naphthalenyl-1-ylidene)bis(sulfamoyl-4,1-phenylene)]diacetamide Fatty acyl CoA synthetase Hexanoyl-CoA synthetase Fatty acid thiokinase (long chain) Acyl-CoA synthase 3-Hydroxyacyl-CoA synthase Acyl-coenzyme A ligase Fatty acid thiokinase Acyl coenzyme A synthetase Hexanoyl coenzyme A synthetase Fatty acyl-coenzyme A synthetase Fatty acyl-CoA ligase Acyl CoA synthetase E.C. 6.2.1.3 |
| Description | Acyl coenzyme A synthetase (ACS), namely acetyl coenzyme A synthetase, is often used in biochemical research. Acyl coenzyme A synthetase can catalyze the activation of fatty acids by coenzyme A through a two-step thioesterification reaction to produce acyl coenzyme A, and then participate in a variety of anabolic and catabolic lipid metabolism pathways, and participate in the TCA cycle in aerobic respiration[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C26H22N4O7S2 |
|---|---|
| Appearance | powder | white |
| Storage condition | −20°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;type N95 (US);type P1 (EN143) respirator filter |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |