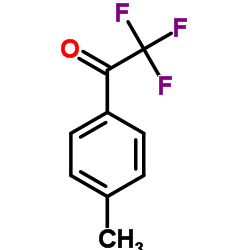
9025-13-2
| Name | Creatininase |
|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Creatinine amidohydrolase
2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-p-tolyl-ethanone 2,2,2-Trifluoro-1-(4-methylphenyl)ethanone Creatinine amide hydrolase Native Pseudomonas sp. Creatinine amidohydrolase |
| Description | Creatininase (Creatinine amidohydrolase; CAH), namely creatinine amidohydrolase, from Pseudomonas putida, is a homohexameric enzyme commonly used in biochemical research. Creatininase acts on carbon-nitrogen bonds other than peptide bonds, and can catalyze the hydrolysis of creatinine to creatine, which can then be metabolized by creatinase to urea and sarcosine[1]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| References |
| Density | 1.2±0.1 g/cm3 |
|---|---|
| Boiling Point | 194.5±35.0 °C at 760 mmHg |
| Molecular Formula | C9H7F3O |
| Molecular Weight | 188.146 |
| Flash Point | 78.1±17.4 °C |
| Exact Mass | 188.044907 |
| LogP | 2.61 |
| Appearance | lyophilized powder |
| Vapour Pressure | 0.4±0.4 mmHg at 25°C |
| Index of Refraction | 1.453 |
| Storage condition | 2-8°C |
| Personal Protective Equipment | Eyeshields;Gloves;half-mask respirator (US);multi-purpose combination respirator cartridge (US) |
|---|---|
| Safety Phrases | 22-24/25 |
| RIDADR | NONH for all modes of transport |
| WGK Germany | 3 |