Vonoprazan hydrochloride
Modify Date: 2024-01-05 12:11:56
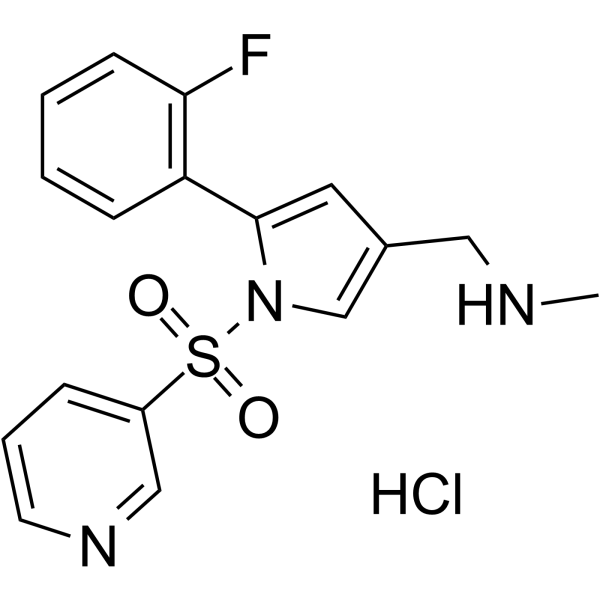
Vonoprazan hydrochloride structure
|
Common Name | Vonoprazan hydrochloride | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| CAS Number | 1957202-44-6 | Molecular Weight | 381.85 | |
| Density | N/A | Boiling Point | N/A | |
| Molecular Formula | C17H17ClFN3O2S | Melting Point | N/A | |
| MSDS | N/A | Flash Point | N/A | |
Use of Vonoprazan hydrochlorideVonoprazan hydrochloride, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), is a potent and orally active potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB), with antisecretory activity. Vonoprazan hydrochloride inhibits H+,K+-ATPase activity in porcine gastric microsomes with an IC50 of 19 nM at pH 6.5. Vonoprazan hydrochloride is developed for the research of acid-related diseases, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease. Vonoprazan hydrochloride can be used for eradication of Helicobacter pylori[1][2][3]. |
| Name | Vonoprazan hydrochloride |
|---|
| Description | Vonoprazan hydrochloride, a proton pump inhibitor (PPI), is a potent and orally active potassium-competitive acid blocker (P-CAB), with antisecretory activity. Vonoprazan hydrochloride inhibits H+,K+-ATPase activity in porcine gastric microsomes with an IC50 of 19 nM at pH 6.5. Vonoprazan hydrochloride is developed for the research of acid-related diseases, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease and peptic ulcer disease. Vonoprazan hydrochloride can be used for eradication of Helicobacter pylori[1][2][3]. |
|---|---|
| Related Catalog | |
| Target |
IC50: 19 nM (porcine gastric H+,K+-ATPase, at pH 6.5)[2] |
| In Vitro | Vonoprazan (0.1 nM-10 μM; 30 minutes) exhibits porcine gastric H+, K+-ATPase activity in a concentration-dependent manner[2]. Vonoprazan does not inhibit Na+,K+-ATPase activity, even at concentrations 500 times higher than their IC50 values against gastric H+,K+-ATPase activity[2]. |
| In Vivo | Vonoprazan (1-4 mg/kg; p.o.) completely inhibits basal and 2-deoxy-D-glucose (200 mg/kg; s.c.)-stimulated gastric acid secretion at the 4 mg/kg dose in rats[2]. Animal Model: Male 7- or 8-week-old Sprague-Dawley rat[2] Dosage: 0.5 mg/kg, 1 mg/kg, 2 mg/kg, 4 mg/kg Administration: Oral administration Result: Inhibited basal gastric acid secretion in a dose-dependent manner. |
| References |
| Molecular Formula | C17H17ClFN3O2S |
|---|---|
| Molecular Weight | 381.85 |