Aneuploidy in Drosophila, II. Further validation of the FIX and ZESTE genetic test systems employing female Drosophila melanogaster.
C Osgood, S Zimmering, J M Mason
Index: Mutat. Res. 259(2) , 147-63, (1991)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Two sensitive genetic systems for the detection of germline aneuploidy employing Drosophila melanogaster females were described in the first paper of this series (Zimmering et al., submitted to Mutation Research). Designated FIX and ZESTE, these systems permit the rapid and efficient detection of exceptional offspring derived from aneuploid female germ cells. The current report presents test results from a survey of 8 additional chemicals that have been analyzed in both systems. The tested chemicals include: acetonitrile, cadmium chloride, carbendazim, dimethylsulfoxide (DMSO), methylmercury(II) chloride, methoxyethyl acetate, propionitrile and water. Excluding the negative control, water, only the fungicide carbendazim failed to induce aneuploidy in either test system. Of the remaining 6 chemicals one, methylmercury(II) chloride, was positive in the FIX system but not in ZESTE, while MEA was positive in ZESTE and borderline in FIX. The results provide little evidence of germ-cell stage specificity of response to the tested chemicals. Comparison of the induced rates of aneuploidy i indicates that these can exhibit departures from simple additivity to the spontaneous rates: induced rates in the ZESTE system are generally higher and more variable than those from FIX. Possible reasons for the difference in responsiveness between FIX and ZESTE flies are discussed as is the question of the classification of those chemicals which induce chromosome loss events but not chromosome gains.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
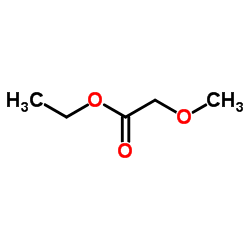 |
Ethyl methoxyacetate
CAS:3938-96-3 |
C5H10O3 |
|
Molecular basis for the enhanced lipase-catalyzed N-acylatio...
2006-11-01 [ChemBioChem. 7(11) , 1745-9, (2006)] |
|
Hydration structure of poly(2-methoxyethyl acrylate): compar...
2010-01-01 [J. Biomater. Sci. Polym. Ed. 21(14) , 1925-35, (2010)] |
|
Reagents for (ir)reversible enzymatic acylations.
2003-07-21 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 1(14) , 2405-15, (2003)] |
|
Enzymatic enantiomeric resolution of phenylethylamines struc...
2011-12-07 [Org. Biomol. Chem. 9(23) , 8171-7, (2011)] |
|
Application of automated matrix-assisted laser desorption/io...
2001-01-01 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 15(15) , 1327-33, (2001)] |