Effects of the lipid regulator drug gemfibrozil: A toxicological and behavioral perspective.
Jorge F Henriques, Ana Rita Almeida, Thayres Andrade, Olga Koba, Oksana Golovko, Amadeu M V M Soares, Miguel Oliveira, Inês Domingues
Index: Aquat. Toxicol. 170 , 355-64, (2016)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Pharmaceuticals are emerging contaminants as their worldwide consumption increases. Fibrates such as gemfibrozil (GEM) are used in human medicine to reduce blood concentrations of cholesterol and triacylglycerol and also are some of the most frequently reported pharmaceuticals in waste waters and surface waters. Despite some studies have already demonstrated the negative impact in physiological and/or reproductive endpoints in adult fish, data on survival and behavioral effects in fish larvae are lacking. This study aimed to assess the effects of GEM on zebrafish eleutheroembryo development and locomotor behavior. A fish embryo toxicity (FET) test was undertaken to evaluate GEM acute toxicity by exposing embryos to 0, 6.58, 9.87, 14.81, 22.22, 33.33 and 50mg/L. Developmental endpoints such as hatching success, edemas and malformations were recorded. A second test was undertaken by exposing embryos to 0, 1.5, 3 and 6mg/L in order to evaluate the effects of GEM on 120 and 144h post fertilization (hpf) larvae locomotor activity by video tracking, using a Zebrabox(®) (Viewpoint, France) device. From the data recorded, several parameters such as total swimming distance (TSD) and total swimming time (TST) in each 120s integration time were calculated. Data showed that this compound has a moderate toxic effect on fish embryo development, affecting both survival and hatching success with a calculated 96h LC50 of 11.01mg/L and no effects at the developmental level at 6mg/L. GEM seems to impair locomotor activity, even at concentrations where developmental abnormalities were unperceived, at concentrations as low as 1.5mg/L. Both TSD and TST were sensitive to GEM exposure. These effects do not seem to be independent of the developmental stage as 120hpf larvae seem to present a development bias with repercussions in locomotor behavior. This study highlights the need to include behavioral endpoints in ecotoxicological assays as this seems to be a more sensitive endpoint often disregarded. Copyright © 2015 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
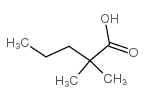 |
2,2-dimethylvaleric acid
CAS:1185-39-3 |
C7H14O2 |
|
Liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric assay for quantitat...
2008-02-01 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 862(1-2) , 168-74, (2008)] |
|
Effects of branched-chain fatty acids on GABA-degradation an...
1980-12-01 [Pharmacol. Biochem. Behav. 13(6) , 843-9, (1980)] |
|
Oxidative metabolism of 4-aminobutyrate by rat brain mitocho...
1980-01-01 [J. Neurochem. 34(1) , 197-202, (1980)] |