Analogues of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid and sodium fluoride as anticoagulants.
M Narita, M Hino, T Takubo, N Tatsumi
Index: Osaka City Med. J. 46(1) , 71-87, (2000)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Three analogues of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (EDTA), ethyleneglycoltetraacetic acid (EGTA), ethylendiaminedipropionic acid (EDDP), and hexamethylenediaminetetraacetic acid (HDTA), and sodium fluoride (NaF) were evaluated as anticoagulants used for rapid and multi-parametric analysis with minimal amounts of blood. EDDP and HDTA induced rapid blood coagulation (< 30 min), while NaF was not useful for coagulation tests because no coagulation was observed by addition of PT- or APTT-reagents. EGTA could be used for hematology and coagulation tests, although platelet count was significantly decreased in comparison with EDTA treated blood due to platelet aggregation, although prothrombin time was prolonged with EGTA-treated blood. Platelet aggregation could be prevented by addition of kanamycin. In chemistry tests, correlations between serum values and EGTA and kanamycin treated plasma values were good for all items. Based on these findings, we concluded that EGTA could be used for hematology, coagulation, and chemistry tests, although with some limitations.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
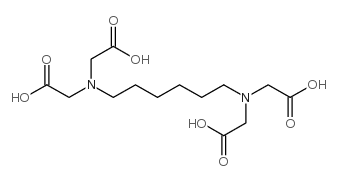 |
1,6-Diaminohexane-N,N,N',N'-tetraacetic Acid
CAS:1633-00-7 |
C14H24N2O8 |
|
Effects of osmolality and ionic strength on the mechanism of...
1993-05-01 [J. Physiol. 464 , 629-48, (1993)] |
|
Effects of Mg2+ on Ca2+ release from sarcoplasmic reticulum ...
2000-07-15 [J. Physiol. 526 Pt 2 , 299-312, (2000)] |
|
Developmental changes in the activation properties and ultra...
1999-04-01 [J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 20(3) , 249-64, (1999)] |
|
Tetragonal deformation of the hexagonal myofilament matrix i...
1992-10-01 [J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 13(5) , 573-80, (1992)] |
|
Chelation in metal intoxication. VIII. Removal of chromium f...
1980-03-01 [Clin. Toxicol. 16(1) , 33-40, (1980)] |