Isolation, identification and bacterial mutagenicity of 2-nitro-9-fluorenone from diesel-exhaust particle extracts.
W E Bechtold, T R Henderson, A L Brooks
Index: Mutat. Res. 173(2) , 105-9, (1986)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Organic extracts of diesel-exhaust particles show direct mutagenic activity in the Salmonella typhimurium bacterial mutagenicity assay. Nitro-aromatic compounds are believed to be responsible for part of the mutagenicity. A previously unidentified polyfunctional nitro-aromatic compound, 2-nitro-9-fluorenone (2N-Fone) was isolated from diesel-exhaust particles using a two-step fractionation scheme consisting of Sephadex LH20 chromatography and silica-gel thin-layer chromatography. Positive identification was by gas chromatography/mass spectroscopy and coelution with an authentic standard. Direct and indirect mutagenicities of 2N-Fone in several bacterial strains were also determined. The results indicated that 2N-Fone produces 60-70 rev/nmole of direct mutagenic activity, and is about 1/5 to 1/10 as mutagenic as 1-nitropyrene.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
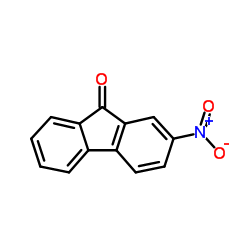 |
2-Nitro-9-fluorenone
CAS:3096-52-4 |
C13H7NO3 |
|
Laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry...
1996-07-15 [Anal. Chem. 68(14) , 2319-24, (1996)] |
|
2-Nitrofluorene and related compounds: prevalence and biolog...
1988-09-01 [Mutat. Res. 196(2) , 177-209, (1988)] |
|
Voltammetric Determination of Genotoxic Nitro Derivatives of...
[Electroanalysis 22(17-18) , 2034-2042, (2010)] |
|
2-Nitrofluoren-9-one: a unique mutagen formed in the photo-o...
1986-03-01 [Carcinogenesis 7(3) , 499-502, (1986)] |
|
In-vitro mutagenic potential and effect on permeability of c...
2006-11-01 [J. Pharm. Pharmacol. 58(11) , 1545-52, (2006)] |