Calycosin stimulates proliferation of estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer cells through downregulation of Bax gene expression and upregulation of Bcl-2 gene expression at low concentrations.
Jian Chen, Wen-bi Xiong, Yao Xiong, Yi-ying Wu, Xia-jing Chen, Zheng-jun Shao, Li-tao Liu, Wen-juan Kuang, Xian-shu Tan, Li-ming Zhou
Index: J. Parenter. Enteral Nutr. 35 , 763-769, (2011)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Calycosin is one of main components in the herb radix astragali and is considered a typical phytoestrogen. It has either estrogenic or antiestrogenic effects that mainly depend on estrogen levels in vivo. This study investigated the effects and mechanisms of calycosin on estrogen receptor (ER)-positive human breast cancer (MCF-7) cells in vitro.ER-positive MCF-7 cells were treated with different concentrations of calycosin. Effects of calycosin on the proliferation of ER-positive MCF-7 cells were determined by the MTT assay. Apoptosis in these treated cells was examined by flow cytometry. The mRNA and protein levels of Bcl-2 and Bax in these treated cells were also determined by reverse-transcription polymerase chain reaction and immunohistochemical staining, respectively.Compared with the vehicle control, calycosin stimulated proliferation of ER-positive MCF-7 cells at low concentrations (2, 4, and 8 µmol/L). Furthermore, at these concentrations, calycosin decreased the percentage of early apoptosis in MCF-7 cells, downregulated mRNA and protein levels of Bax, and upregulated those of Bcl-2 at low concentrations. On the other hand, calycosin at higher concentrations (16 and 32 µmol/L) inhibited cell proliferation.At relatively low concentrations, calycosin has stimulatory effects on the proliferation of MCF-7 cells, with the estrogenic effect the mechanism.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
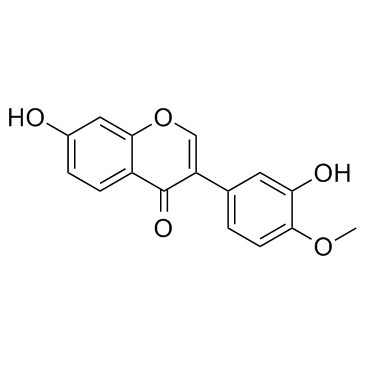 |
Calycosin
CAS:20575-57-9 |
C16H12O5 |
|
Thermal stability of kudzu root (Pueraria Radix) isoflavones...
2015-03-01 [J. Food Sci. Technol. 52(3) , 1578-85, (2015)] |
|
Calycosin orchestrates the functions of Danggui Buxue Tang, ...
2015-06-20 [J. Ethnopharmacol. 168 , 150-7, (2015)] |
|
Protective effects of calycosin against CCl4-induced liver i...
2015-02-01 [Pharm. Res. 32(2) , 538-48, (2015)] |
|
Neuroprotective effect of calycosin on cerebral ischemia and...
2012-12-18 [J. Ethnopharmacol. 144 , 768-774, (2012)] |
|
Calycosin protects HUVECs from advanced glycation end produc...
2011-09-01 [J. Ethnopharmacol. 137 , 359-370, (2011)] |