Magnesium, essential for base excision repair enzymes, inhibits substrate binding of N-methylpurine-DNA glycosylase.
Sanjay Adhikari, Jeffery A Toretsky, Linshan Yuan, Rabindra Roy
Index: J. Biol. Chem. 281(40) , 29525-32, (2006)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
N-Methylpurine-DNA glycosylase (MPG) initiates base excision repair in DNA by removing a wide variety of alkylated, deaminated, and lipid peroxidation-induced purine adducts. MPG activity and other DNA glycosylases do not have an absolute requirement for a cofactor. In contrast, all downstream activities of major base excision repair proteins, such as apurinic/apyrimidinic endonuclease, DNA polymerase beta, and ligases, require Mg(2+). Here we have demonstrated that Mg(2+) can be significantly inhibitory toward MPG activity depending on its concentration but independent of substrate type. The pre-steady-state kinetics suggests that Mg(2+) at high but physiologic concentrations decreases the amount of active enzyme concentrations. Steady-state inhibition kinetics showed that Mg(2+) affected K(m), but not V(max), and the inhibition could be reversed by EDTA but not by DNA. At low concentration, Mg(2+) stimulated the enzyme activity only with hypoxanthine but not ethenoadenine. Real-time binding experiments using surface plasmon resonance spectroscopy showed that the pronounced inhibition of activity was due to inhibition in substrate binding. Nonetheless, the glycosidic bond cleavage step was not affected. These results altogether suggest that Mg(2+) inhibits MPG activity by abrogating substrate binding. Because Mg(2+) is an absolute requirement for the downstream activities of the major base excision repair enzymes, it may act as a regulator for the base excision repair pathway for efficient and balanced repair of damaged bases, which are often less toxic and/or mutagenic than their subsequent repair product intermediates.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
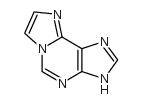 |
1,N6-ETHENOADENINE
CAS:13875-63-3 |
C7H5N5 |
|
Measurement of urinary excretion of 5-hydroxymethyluracil in...
2005-03-15 [Toxicol. Lett. 155(3) , 403-10, (2005)] |
|
Highly mutagenic exocyclic DNA adducts are substrates for th...
2012-01-01 [PLoS ONE 7(12) , e51776, (2012)] |
|
Modeling the chemical step utilized by human alkyladenine DN...
2011-10-12 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 133(40) , 16258-69, (2011)] |
|
Structural insights by molecular dynamics simulations into d...
2002-09-01 [Nucleic Acids Res. 30(17) , 3778-87, (2002)] |
|
Analysis of substrate specificity of Schizosaccharomyces pom...
2011-12-01 [EMBO Rep. 12(12) , 1286-92, (2011)] |