Transection of carotid sinus nerve inhibits the turnover of dopamine and norepinephrine in long-term hypoxic carotid bodies: a biochemical and morphometric study.
J M Pequignot, S Hellström, S Forsgren, J M Cottet-Emard, L Peyrin
Index: J. Auton. Nerv. Syst. 32(2) , 165-76, (1991)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To assess the efferent influence of the carotid sinus nerve on the catecholamine function and the vascularity in long-term hypoxic carotid bodies, rats were exposed to hypoxia (10% O2 in nitrogen for 1 and 3 weeks) after unilateral transection of the sinus nerve. In the intact carotid bodies, long-term hypoxia elicited several biochemical and morphological alterations: increased turnover of dopamine and norepinephrine, increased volume density of blood vessels, decreased volume density of glomic tissue. Transection of the sinus nerve reduced but did not abolish the increase in turnover of dopamine and norepinephrine evoked by hypoxia without preventing the structural alterations. Immunocytochemical studies revealed the presence of nerve fibres exhibiting neuropeptide Y-like immunoreactivity which persisted after the excision of the carotid sinus nerve. Nerve fibres showing substance P-like immunoreactivity were found in the intact carotid bodies but not in the carotid bodies deprived of sinus nerve. It is concluded that the sinus nerve exerts a stimulatory efferent control on the synthesis and release of dopamine and norepinephrine in rat carotid body during long-term hypoxia, but no appreciable vasodilatory influence on the glomic vasculature. A possible role of substance P contained in the endings of the carotid sinus nerve is discussed.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
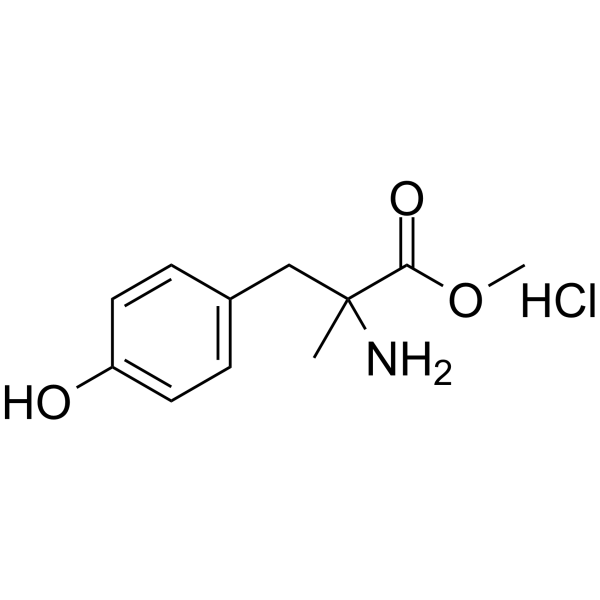 |
alpha-methyl-dl-tyrosine methyl ester hydrochloride
CAS:7361-31-1 |
C11H16ClNO3 |
|
Chemical genetics reveals a complex functional ground state ...
2007-05-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 3(5) , 268-273, (2007)] |
|
Genetic mapping of targets mediating differential chemical p...
2009-10-01 [Nat. Chem. Biol. 5 , 765-71, (2009)] |
|
Evidence in locomotion test for the functional heterogeneity...
2004-01-01 [Br. J. Pharmacol. 141(1) , 132-40, (2004)] |
|
Conditional mouse mutants highlight mechanisms of corticotro...
2008-11-01 [Mol. Psychiatry 13(11) , 1028-42, (2008)] |
|
The dopamine D3-receptor: a postsynaptic receptor inhibitory...
[J. Neural Transm. Gen. Sect. 94 , 11-19, (1993)] |