Biodegradation of the sulfonylurea herbicide chlorimuron-ethyl by the strain Pseudomonas sp. LW3.
Ji-Ping Ma, Zhe Wang, Peng Lu, Hui-jie Wang, Shinawar Waseem Ali, Shun-Peng Li, Xing Huang
Index: FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 296(2) , 203-9, (2009)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The chlorimuron-ethyl-degrading bacterium LW3 was isolated from contaminated soil and identified by 16S rRNA gene sequencing as Pseudomonas sp. When chlorimuron-ethyl was provided as the sole nitrogen source, the degradation efficiency in liquid medium was about 81.0% after 7 days of inoculation with strain LW3. The effects of chlorimuron-ethyl concentration and temperature on biodegradation were examined. Two metabolites of degradation were analyzed by LC/MS. Based on the identified products, strain LW3 seemed to be able to degrade chlorimuron-ethyl by cleavage of the sulfonylurea bridge. The inoculation of strain LW3 to chlorimuron-ethyl-treated soil resulted in a higher degradation rate than in uninoculated soil, regardless of the soil being sterilized or nonsterilized. This microbial culture has great potential for the bioremediation of soil contaminated with chlorimuron-ethyl.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
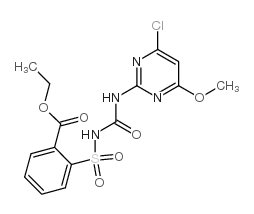 |
Chlorimuron-ethyl
CAS:90982-32-4 |
C15H15ClN4O6S |
|
Response of multiple seeded cocklebur and other cocklebur ty...
2005-07-01 [Pest Manag. Sci. 61(7) , 643-8, (2005)] |
|
Magnetic solid-phase extraction of sulfonylurea herbicides i...
2012-10-17 [Anal. Chim. Acta 747 , 29-35, (2012)] |
|
Elucidating the specificity of binding of sulfonylurea herbi...
2005-02-22 [Biochemistry 44(7) , 2330-8, (2005)] |
|
Examination of the translocation of sulfonylurea herbicides ...
2010-11-30 [Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. 24(22) , 3309-19, (2010)] |
|
Single and joint effects of pesticides and mercury on soil u...
2007-01-01 [J. Environ. Sci. (China) 19(2) , 210-6, (2007)] |