Effects of thyroxine and its related compounds on cerebral GABA receptors: inhibitory action on benzodiazepine recognition site in GABAA receptor complex.
R Narihara, M Hirouchi, T Ichida, K Kuriyama, E Roberts
Index: Neurochem. Int. 25(5) , 451-4, (1994)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The effects of thyroxine and its related derivatives on gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) receptors in the rat brain were examined. D-Thyroxine strongly inhibited [3H]flunitrazepam binding to benzodiazepine receptor in crude synaptic membrane from the rat brain. The Scatchard analysis of the [3H]flunitrazepam binding in the presence of D-thyroxine indicated the decreases in the affinity and maximum number of binding site. Furthermore, D-thyroxine inhibited the enhancing effect of flunitrazepam on GABA-stimulated 36Cl- influx into membrane vesicles, although GABA-stimulated 36Cl- influx alone was not affected by D-thyroxine. On the other hand, the effects of thyroxine and its related derivatives on cerebral GABAB receptor binding were not noted. These results suggest that D-thyroxine may be a drug which is able to modulate the function of GABAA receptor complex via the inhibitory action on benzodiazepine recognition site.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
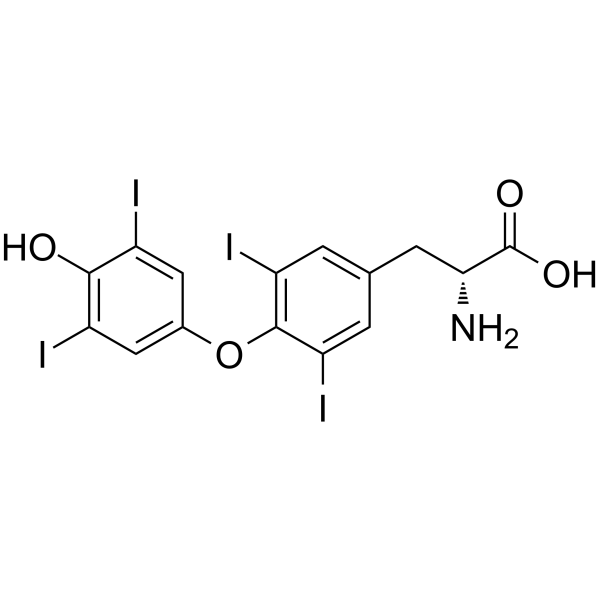 |
Dextrothyroxine
CAS:51-49-0 |
C15H11I4NO4 |
|
Design of mechanism-based inhibitors of transthyretin amyloi...
2007-11-15 [J. Med. Chem. 50 , 5589-99, (2007)] |
|
Maintenance of brain thyroid hormone level during peripheral...
2006-09-05 [Life Sci. 79(15) , 1450-5, (2006)] |
|
Dextrothyroxine in the treatment of generalized thyroid horm...
1992-04-01 [Thyroid 2(1) , 15-9, (1992)] |
|
Treatment of pituitary resistance to thyroid hormone (PRTH) ...
1996-03-01 [Acta Paediatr. 85(3) , 387-90, (1996)] |
|
A novel resistance to thyroid hormone associated with a new ...
1999-02-01 [Thyroid 9(2) , 165-71, (1999)] |