β(1,3)-glucan synthase complex from Alternaria infectoria, a rare dematiaceous human pathogen.
Jorge Anjos, Chantal Fernandes, Branca M A Silva, Célia Quintas, Alexandra Abrunheiro, Neil A R Gow, Teresa Gonçalves
Index: Med. Mycol 50(7) , 716-25, (2012)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The fungal cell wall polymer β-(1,3)-D-glucan is synthesized by the enzyme β-(1,3)- D-glucan synthase that is a complex composed of at least two proteins, Rho1p and Fks1p. Here, we report the nucleotide sequence of a single FKS gene and of the regulatory unit, RHO1 from the dematiaceous pathogenic fungus Alternaria infectoria. The predicted AiFks and AiRho share, respectively, 93% and 100% identity with that of Drechslera tritici-repentis. We also report that the sensitivity to caspofungin of eight different A. infectoria clinical strains is similar, with a MIC > 32 µg/ml and a MEC of 1 µg/ml, except for one strain which had a MEC of 1.4 µg/ml. This same strain exhibited one substitution at the hot spot 2, S1405A, compatible with less susceptible phenotypes, with the other seven strains having no mutations in either hot spot 1 or 2. The relative quantification of the expression of AiFKS and of AiRHO demonstrated a decrease in response to an exposure to caspofungin at 0.5 µg/ml.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
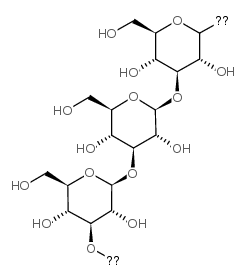 |
β-1,3-Glucan
CAS:9051-97-2 |
C18H30O15 |
|
How carbohydrates sculpt cells: chemical control of morphoge...
2013-09-01 [Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 11(9) , 648-55, (2013)] |
|
An initial event in the insect innate immune response: struc...
2013-01-08 [Biochemistry 52(1) , 161-70, (2013)] |
|
Interleukin-23 mediates the intestinal response to microbial...
2014-07-01 [Arthritis Rheumatology 66(7) , 1755-67, (2014)] |
|
Extracellular cell wall β(1,3)glucan is required to couple s...
2013-10-28 [J. Cell Biol. 203(2) , 265-82, (2013)] |
|
Soluble β-1,3/1,6-glucan in seaweed from the southern hemisp...
2013-01-30 [Carbohydr. Polym. 92(1) , 241-8, (2013)] |