The electrophysiological effects of melatonin and a putative melatonin antagonist (N-acetyltryptamine) on rat suprachiasmatic neurones in vitro.
R Mason, A Brooks
Index: Neurosci. Lett. 95(1-3) , 296-301, (1988)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Several studies have implicated the suprachiasmatic nuclei (SCN) as a target for the action of melatonin in its regulation of seasonal and circadian behaviour. Single-unit activity from the SCN and adjacent paraventricular area and anterior hypothalamus was recorded using the in vitro rat hypothalamic slice preparation. Neurones were tested for responses to iontophoresed or pressure ejected melatonin (n = 62) and serotonin (5-HT, n = 80). The majority (n = 24-26) of melatonin-sensitive SCN neurones were inhibited by melatonin in a dose-dependent manner during the latter portion of the projected light phase of the circadian light-dark cycle. A putative melatonin antagonist, N-acetyltryptamine, exhibited concentration dependent mixed agonist-antagonist effects on melatonin-evoked responses.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
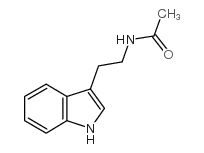 |
N-Acetyltryptamine
CAS:1016-47-3 |
C12H14N2O |
|
Chloroplastic and cytoplasmic overexpression of sheep seroto...
2015-05-01 [J. Pineal Res. 58(4) , 461-9, (2015)] |
|
Serine residues 110 and 114 are required for agonist binding...
2001-04-20 [Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 282(5) , 1229-36, (2001)] |
|
[The biosynthesis of low-molecular-weight nitrogen-containin...
2002-01-01 [Mikrobiologiia 71(6) , 773-7, (2002)] |
|
Melatonin receptor pharmacology: toward subtype specificity.
1997-11-01 [Biol. Cell 89 , 531-537, (1998)] |
|
Serotonin metabolism in rat skin: characterization by liquid...
2004-01-01 [Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 421(1) , 61-6, (2004)] |