| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
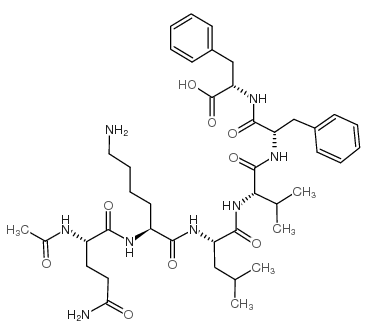 |
Acetyl-Amyloid β-Protein (15-20) amide trifluoroacetate salt
CAS:189064-06-0 |
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
 |
Acetyl-Amyloid β-Protein (15-20) amide trifluoroacetate salt
CAS:189064-06-0 |