| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Articles |
|---|---|---|
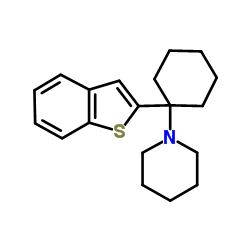 |
BTCP HCl
CAS:112726-66-6 |
|
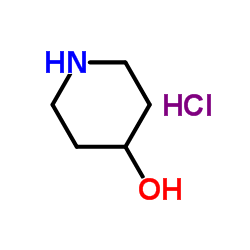 |
Piperidin-4-olhydrochlorid
CAS:5382-17-2 |