The neuroprotective effect of talipexole from paraquat-induced cell death in dopaminergic neuronal cells.
Rubén Gómez-Sánchez, José M Bravo-San Pedro, Mireia Niso-Santano, Germán Soler, José M Fuentes, Rosa A González-Polo, Rubén Gómez-Sánchez, José M. Bravo-San Pedro, Mireia Niso-Santano, Germán Soler, José M. Fuentes, Rosa A. González-Polo
Index: Neurotoxicology 31(6) , 701-8, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Talipexole is a non-ergot dopamine (DA) agonist that has been used in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. In the present study, we examined the effect of talipexole on paraquat (PQ)-induced N27 cell death and the intracellular pathways involved in this effect. Pretreatment of N27 cells with talipexole (1mM) resulted in significant protection against paraquat-induced cell death. In N27 cells, talipexole inhibited paraquat-induced apoptotic hallmarks such as cytochrome c release, caspase-3 activation, chromatin condensation and externalization of phosphatidilserine. Talipexole pretreatment prevents the reduction in the anti-apoptotic Bcl-x(L) protein and increases in the pro-apoptotic form of Bak and p-Bad, both induced by PQ. Finally, we also observed that talipexole abrogates the activation of cell death pathways JNK1/2 and p38 produced by PQ, and increases the phosphorylated (active) forms of the pro-survival pathways ERK1/2 and Akt. These results reveal that talipexole exerts a neuroprotective effect in a mesencephalic cell line exposed to the neurotoxin PQ, which is related to the etiology of Parkinson's disease.Copyright © 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
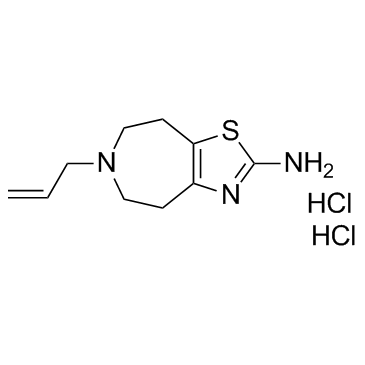 |
B-HT 920
CAS:36085-73-1 |
C10H17Cl2N3S |
|
Duration of drug action of dopamine D2 agonists in mice with...
2015-12-16 [Neuroreport 26 , 1126-32, (2015)] |
|
Mechanism of decongestant activity of alpha 2-adrenoceptor a...
2008-01-01 [Pulm. Pharmacol. Ther. 21(3) , 449-54, (2008)] |
|
Paraquat leads to dopaminergic neural vulnerability in organ...
2003-08-01 [Neurosci. Res. 46(4) , 523-32, (2003)] |
|
Impaired endothelial alpha-2 adrenergic receptor-mediated va...
2002-03-01 [Hypertens. Res. 25(2) , 197-202, (2002)] |
|
Blood pressure and alpha-vascular reactivity in hypertensive...
2004-04-05 [Eur. J. Pharmacol. 489(1-2) , 101-10, (2004)] |