Lactate dehydrogenase-C4 is involved in heparin- and NADH-dependent bovine sperm capacitation.
C M O'Flaherty, N B Beorlegui, M T Beconi
Index: Andrologie 34(2) , 91-7, (2002)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Lactate dehydrogenase C4 isoenzyme (LDH-C4) is involved in the energy metabolism of spermatozoa. Sperm capacitation is considered part of an oxidative process; an NADH oxidase of plasma membrane could be responsible for superoxide anion generation which is required for capacitation. The role of LDH-C4 and the requirements of NADH in cryopreserved bovine sperm capacitation were studied. LDH-C4 activity was 5.52 +/- 3.41, 15.72 +/- 6.04 and 15.22 +/- 1.92 Units 1010 spermatozoa-1 in plasma membrane, sperm suspension and cytosol fraction, respectively; these activities were inhibited by sodium oxamate. To study the influence of oxidative substrates in capacitation, three different TALP (T) media were used: TP (pyruvate); TL (lactate) and TC (citrate); heparin or NADH was then added. There were no significant differences in the percentage of capacitation induced by heparin or NADH in TALP medium; similar levels of capacitation were achieved with TL alone or TL +heparin and TP +NADH; capacitation was inhibited with sodium oxamate in all treatments used. Cytosolic NADH may be required as a substrate for sperm oxidase. Lactate influx through plasma membrane may be utilized by cytosolic LDH-C4, increasing reduced coenzymes required for capacitation. Plasma membrane LDH-C4 may participate in the production of lactate to obtain intracellular reducing equivalents to be used by sperm oxidase for in vitro sperm capacitation.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
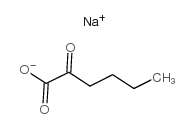 |
2-KETOHEXANOIC ACID SODIUM SALT
CAS:13022-85-0 |
C6H9NaO3 |
|
Calcium uptake by bovine epididymal spermatozoa is regulated...
1989-04-01 [Biol. Reprod. 40(4) , 744-51, (1989)] |
|
Inhibition studies on LDH isoenzyme purified from Uromastix ...
1996-01-01 [J. Enzym. Inhib. 10(3) , 187-93, (1996)] |
|
GC-MS profiling of urinary organic acids evaluated as a quan...
1996-10-01 [Clin. Chem. 42(10) , 1609-15, (1996)] |
|
The stimulus-secretion coupling of amino acid-induced insuli...
1981-09-18 [Biochim. Biophys. Acta 677(1) , 32-8, (1981)] |
|
[Inhibition of postoperative muscular proteolysis by sodium ...
1985-01-01 [Ann. Fr. Anesth. Reanim. 4(4) , 351-4, (1985)] |