The effect of the isomers of alpha-cholorohydrin and racemic beta-chlorolactate on the rat kidney.
K E Porter, A R Jones
Index: Chem. Biol. Interact. 41(1) , 95-104, (1982)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
The (R)- and (S)-isomers of the male antifertility agent alpha-chlorohydrin have been synthesized. When administered to rats, the (R)-isomer induced a period of diuresis and glucosuria, whereas the (S)-isomer, which possesses the antifertility activity, had no detrimental action on the kidney. Neither of the isomers of alpha-chlorohydrin nor those of an active analogue, 3-amino-1-chloropropan-2-ol, had any inhibitory activity on the oxidative metabolism of glucose or lactate in isolated kidney tubules. However, beta-chlorolactate, a metabolite common to both compounds, inhibited the oxidation of glucose, lactate, pyruvate and glutamate to CO2. It is proposed that the antifertility action of the (S)-isomers of alpha-chlorohydrin and 3-amino-1-chloropropan-2-ol is unrelated to the renal toxicity of the (R)-isomers, a toxic action involving the inhibition of oxidative metabolism by (S)-beta-chlorolactate or a further product of this metabolite.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
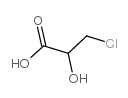 |
β-Chlorolactic acid
CAS:1713-85-5 |
C3H5ClO3 |
|
Oxidative metabolic activity of boar spermatozoa: a system f...
1989-01-01 [Reprod. Fertil. Dev. 1(4) , 357-67, (1989)] |
|
The renal toxicity of (R)-3-chlorolactate in the rat.
1987-01-01 [Chem. Biol. Interact. 62(2) , 157-66, (1987)] |
|
Is the nephrotoxicity of (R)-3-chlorolactate in the rat caus...
1988-12-01 [Xenobiotica 18(12) , 1389-99, (1988)] |
|
Immunotoxic effect of beta-chlorolactic acid on murine splen...
2005-06-01 [Toxicology 210(2-3) , 175-87, (2005)] |