Anti-HIV-1 activity of elafin depends on its nuclear localization and altered innate immune activation in female genital epithelial cells.
Anna G Drannik, Kakon Nag, Xiao-Dan Yao, Bethany M Henrick, T Blake Ball, Francis A Plummer, Charles Wachihi, Joshua Kimani, Kenneth L Rosenthal
Index: PLoS ONE 7 , e52738, (2013)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Elafin (E) and its precursor trappin-2 (Tr) are alarm antiproteases with antimicrobial and immunomodulatory activities. Tr and E (Tr/E) have been associated with HIV-1 resistance. We recently showed that Tr/E reduced IL-8 secretion and NF-κB activation in response to a mimic of viral dsRNA and contributed to anti-HIV activity of cervicovaginal lavage fluid (CVL) of HIV-resistant (HIV-R) commercial sex workers (CSWs). Additionally, Tr, and more so E, were found to inhibit attachment/entry and transcytosis of HIV-1 in human endometrial HEC-1A cells, acting through virus or cells. Given their immunomodulatory activity, we hypothesized that Tr/E could exert anti-HIV-1 activity at multiple levels. Here, using tagged and untagged Tr/E proteins, we comparatively evaluated their protease inhibitory, anti-HIV-1, and immunomodulatory activities, and cellular distribution. E appeared to function as an autocrine/paracrine factor in HEC-1A cells, and anti-HIV-1 activity of E depended on its unmodified N-terminus and altered cellular innate activation, but not its antiprotease activity. Specifically, exogenously added N-terminus-unmodified E was able to enter the nucleus and to reduce viral attachment/entry and transcytosis, preferentially affecting R5-HIV-1(ADA), but not X4-HIV-1(IIIB). Further, anti-HIV-1 activity of E was associated with significantly decreased HIV-1-triggered IL-8 release, attenuated NF-κB/p65 nuclear translocation, and significantly modulated mRNA expression of innate sensors TLR3 and RIG-I in HEC-1A cells. Most importantly, we found that elevated Tr/E in CVLs of HIV-R CSWs were associated with lower mRNA levels of TLRs 2, 3, 4 and RIG-I in the genital ECs from this cohort, suggesting a link between Tr/E, HIV-1 resistance and modulated innate viral recognition in the female genital mucosa. Collectively, our data indicate that unmodified N-terminus is critical for intranuclear localization and anti-HIV-1 activity of E. We also propose that E-mediated altered cellular innate activation most likely contributes to the HIV-R phenotype of these subjects.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
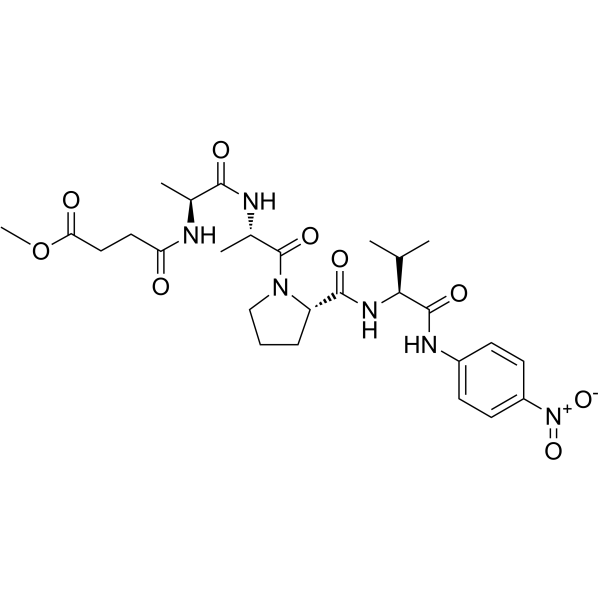 |
MeOSuc-Ala-Ala-Pro-Val-pNA
CAS:70967-90-7 |
C27H38N6O9 |
|
Thrombospondin-1 restrains neutrophil granule serine proteas...
2015-07-01 [Mucosal Immunol. 8 , 896-905, (2015)] |
|
Neutrophil extracellular traps directly induce epithelial an...
2012-01-01 [PLoS ONE 7 , e32366, (2012)] |
|
Inhibition of elastase by a synthetic cotton-bound serine pr...
1999-01-01 [Wound Repair Regen. 7(2) , 106-18, (1999)] |
|
Mapping the extended substrate binding site of cathepsin G a...
1979-05-25 [J. Biol. Chem. 254 , 4027, (1979)] |
|
Effect of cadmium chloride exposure during the induction of ...
2015-08-05 [Chem. Biol. Interact. 238 , 55-65, (2015)] |