Characteristics of white cell-reduced red cells stored in tri-(2-ethylhexyl)trimellitate plastic.
R J Davey, W A Heaton, L T Sweat, N M Stec, E J Nelson, S Holme
Index: Transfusion 34(10) , 895-8, (1994)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
Standard blood storage containers contain extractable plasticizers that accumulate in blood during storage and are an unintended transfusion product. However, extractable plasticizers have a protective effect on the red cell membrane and improve red cell storage variables. Prestorage white cell reduction also improves selected red cell storage variables.The study evaluated whether the beneficial effect of prestorage white cell reduction would offset the negative effect of the absence of extractable plasticizer in red cells stored in AS-3 for 42 days at 4 degrees C. Filtered red cells stored in polyvinylchloride containers with the nonextracting plasticizer, tri-(2-ethylhexyl)trimellitate (TEHTM), were compared to unfiltered red cells stored in polyvinylchloride containers with the extractable plasticizer di-(2-ethylhexyl)phthalate (DEHP).Poststorage supernatant potassium and red cell osmotic fragility were significantly higher in white cell-reduced TEHTM units than in unfiltered DEHP units. The mean 24-hour recovery of the filtered TEHTM red cells was significantly lower than that of the unfiltered DEHP red cells (69.1 +/- 7.4% vs. 77.1 +/- 5.1%, p < 0.05, n = 8).These data demonstrate that white cell reduction before 42-day storage in TEHTM containers with currently approved preservatives does not yield an acceptable red cell component.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
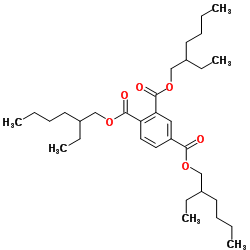 |
UNII:378539Q830
CAS:3319-31-1 |
C33H54O6 |
|
Quantification of five plasticizers used in PVC tubing throu...
2014-08-15 [J. Chromatogr. B. Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 965 , 158-63, (2014)] |
|
Analysis of non-phthalates plasticizers on porous graphitic ...
2014-09-12 [J. Chromatogr. A. 1359 , 277-86, (2014)] |
|
Lack of sensitization for trimellitate, phthalate, terephtha...
2003-04-01 [Food Chem. Toxicol. 41(4) , 589-93, (2003)] |
|
Storage of platelets on flatbed agitators in polyvinyl chlor...
1987-01-01 [Transfusion 27(5) , 399-401, (1987)] |
|
A comparative study of platelets stored in polyvinyl chlorid...
1995-01-01 [Vox Sang. 69(3) , 195-200, (1995)] |