ECG-triggered 18F-fluorodeoxyglucose positron emission tomography imaging of the rat heart is dramatically enhanced by acipimox.
Sylvain Poussier, Fatiha Maskali, Nguyen Tran, Christophe Person, Pablo Maureira, Henri Boutley, Gilles Karcher, Patrick Lacolley, Véronique Régnault, Renaud Fay, Pierre Yves Marie
Index: Eur. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 37(9) , 1745-50, (2010)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
18F-Fluorodeoxyglucose (FDG) imaging, provided by current positron emission tomography (PET) systems dedicated to small animals,might provide a precise functional assessment of the left ventricle (LV) in rats, although conventional metabolic conditioning by hyperinsulinaemic glucose clamping is not well adapted to this setting. This study was aimed at assessing cardiac FDG PET in rats premedicated with acipimox, a potent nicotinic acid derivative yielding comparable image quality to clamping in man.Metabolic conditioning was compared in Wistar rats between a conventional oral glucose loading (1.5 mg/kg) and acipimox, which was given at high but well tolerated doses subcutaneously (25 mg/kg) or orally (50 mg/kg). Myocardial to blood (M/B) activity ratio and myocardial signal to noise (S/N) ratio were analysed on gated FDG PET images.The S/N ratio of the gated cardiac images evolved in parallel with the M/B activity ratio and these two ratios were independently enhanced by glucose loading and acipimox. However, these enhancements were: (1) dramatic for acipimox, especially for the high oral dose of 50 mg/kg (from 2.85 +/- 0.57 to 10.73 +/- 0.54 for the M/B ratio of rats with or without glucose loading; p<0.0001) and (2) much more limited for glucose loading (from 6.61 +/- 0.49 to 7.89 +/- 0.41 for the M/B ratio of rats with or without acipimox administration; p=0.049). With the high oral dose of acipimox, the gated cardiac FDG PET images had very high S/N ratios, at least equivalent to those currently documented in man.Metabolic conditioning by oral doses of acipimox is highly efficient for experimental studies planned with cardiac FDG PET in rats.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
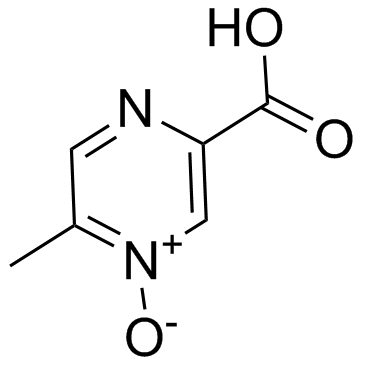 |
Acipimox
CAS:51037-30-0 |
C6H6N2O3 |
|
Kinetics and utilization of lipid sources during acute exerc...
2014-07-15 [Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 307(2) , E199-208, (2014)] |
|
The lowering of hepatic fatty acid uptake improves liver fun...
2008-08-01 [Am. J. Physiol. Endocrinol. Metab. 295(2) , E413-9, (2008)] |
|
Effects of acute and one-week fatty acid lowering on cardiac...
2012-09-01 [J. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 97(9) , 3277-84, (2012)] |
|
The diagnosis of GH deficiency in obese patients: a reapprai...
2010-08-01 [Eur. J. Endocrinol. 163(2) , 201-6, (2010)] |
|
Inhibition of lipolysis in Type 2 diabetes normalizes glucos...
2011-08-01 [Clin. Sci. 121(4) , 169-77, (2011)] |