The ribosome as an entropy trap.
Annette Sievers, Malte Beringer, Marina V Rodnina, Richard Wolfenden
Index: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 101(21) , 7897-901, (2004)
Full Text: HTML
Abstract
To determine the effectiveness of the ribosome as a catalyst, we compared the rate of uncatalyzed peptide bond formation, by the reaction of the ethylene glycol ester of N-formylglycine with Tris(hydroxymethyl)aminomethane, with the rate of peptidyl transfer by the ribosome. Activation parameters were also determined for both reactions, from the temperature dependence of their second-order rate constants. In contrast with most protein enzymes, the enthalpy of activation is slightly less favorable on the ribosome than in solution. The 2 x 10(7)-fold rate enhancement produced by the ribosome is achieved entirely by lowering the entropy of activation. These results are consistent with the view that the ribosome enhances the rate of peptide bond formation mainly by positioning the substrates and/or water exclusion within the active site, rather than by conventional chemical catalysis.
Related Compounds
| Structure | Name/CAS No. | Molecular Formula | Articles |
|---|---|---|---|
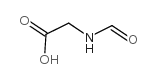 |
N-Formylglycine
CAS:2491-15-8 |
C3H5NO3 |
|
New aldehyde tag sequences identified by screening formylgly...
2008-09-17 [J. Am. Chem. Soc. 130(37) , 12240-1, (2008)] |
|
Function and structure of a prokaryotic formylglycine-genera...
2008-07-18 [J. Biol. Chem. 283(29) , 20117-25, (2008)] |
|
Electron transfer in amino acid.nucleic acid base complexes:...
2006-07-20 [J. Phys. Chem. A 110(28) , 8653-62, (2006)] |
|
A new member of the alkaline phosphatase superfamily with a ...
2008-12-05 [J. Mol. Biol. 384(1) , 120-36, (2008)] |
|
Inhibition of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase by N-formy...
1998-08-01 [J. Enzym. Inhib. 13(5) , 369-76, (1998)] |